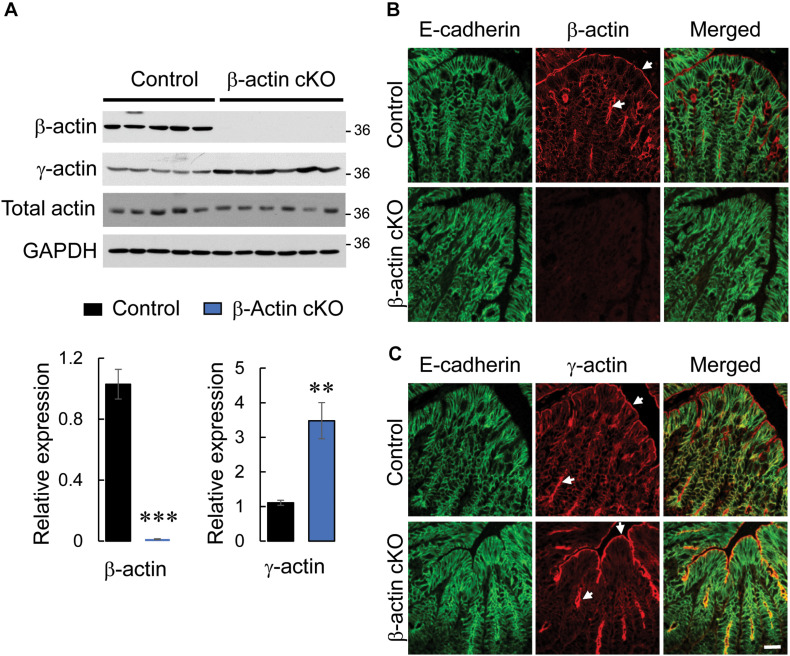
FIGURE 1.
Intestinal epithelial-specific knockout of β-actin in mice results in a compensatory increase in γ-actin expression. (A) Immunoblotting analysis of the expression of cytoplasmic actin isoforms (β-actin and γ-actin) and total actin in colonic epithelial scrapings obtained from control and β-actin cKO mice. Representative immunoblots and densitometric quantification of β-actin and γ-actin expression are shown. Data is presented as a mean ± SE (n = 5); ∗∗p < 0.005, ∗∗∗p < 0.0005. (B,C) Dual immunofluorescence labeling of either β-actin (B) or γ-actin (C) (red) and E-cadherin (green) in full-thickness colonic tissue sections obtained from control and β-actin cKO mice. Arrows indicate the predominant accumulation of both cytoplasmic actin isoforms at the apical pole of colonic epithelial cells. Scale bar, 20 μm.