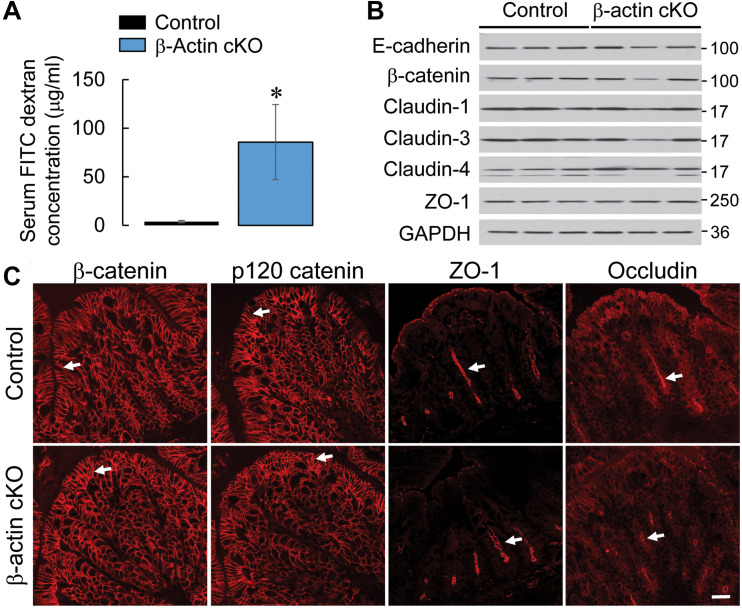
FIGURE 2.
Intestinal epithelial-specific knockout of β-actin increases intestinal permeability without causing significant alterations in the structure and composition of epithelial junctions. (A) Intestinal permeability of control and β-actin cKO mice in vivo was determined by measuring gut-to-blood passage of FITC-dextran. Data is presented as a mean ± SE (n = 5); ∗p < 0.05. (B) Immunoblotting analysis of the expression of selected AJ and TJ proteins in colonic epithelial scrapings obtained from control and β-actin cKO mice. (C) Immunofluorescence labeling and confocal microscopy of AJ (β-catenin and p120 catenin) and TJ (ZO-1, occludin) in colonic sections obtained from control and β-actin cKO mice. Arrows indicate similar localization of junctional proteins in β-actin cKO animals and their control littermates. Scale bar, 20 μm.