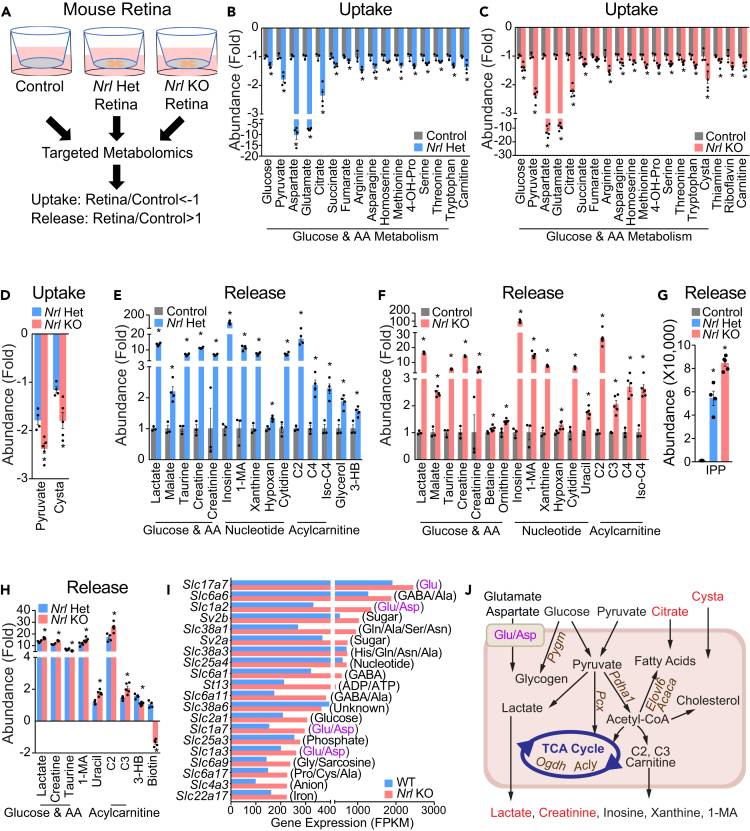
Figure 2.
Metabolite Consumption and Metabolic Gene Expression in Nrl Het (Rod-Dominant) and Nrl KO (all-cone) Mouse Retina
(A) Schematic for profiling medium metabolites in mouse retinal explants. Retinas from Nrl Het and Nrl KO mice were dissected, placed in transwells, and maintained in culture for 24 h. The culture media without retinas were the baseline control. All media metabolites were analyzed by targeted metabolomics.
(B–D) Metabolite consumption from mouse retinal explants. Metabolite uptake in (B) Nrl Het and (C) Nrl KO retinas. (D) The comparison of metabolite uptake between Nrl Het and Nrl KO retinas. Data were relative ion abundance over the control or Nrl Het. N = 6, ∗P < 0.05 versus Control or Nrl Het retinas. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. t test.
(E–H) Metabolite release from mouse retinal explants. Metabolite release in (E) Nrl Het and (F) Nrl KO retinas. (G and H) The comparison of metabolite uptake between Nrl Het and Nrl KO retinas. Data were relative ion abundance over the control or Nrl Het or absolute ion abundance when those metabolites were not detected in the baseline control. N = 6, ∗P < 0.05 versus Control or Nrl Het retinas. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. t test.
(I) Gene expression of the top 20 abundant small molecule transporters in the Nrl KO and Het mouse retinas.
(J) Schematic of nutrient uptake and release in Nrl KO retinas. Metabolites with enhanced uptake or release in Nrl KO retinas are colored red. Upregulated genes in Nrl KO are colored brown. Glu/Asp represents transporters for glutamate and aspartate.
See also Figures S2–S3 and Tables S2, S4, S7, and S10.