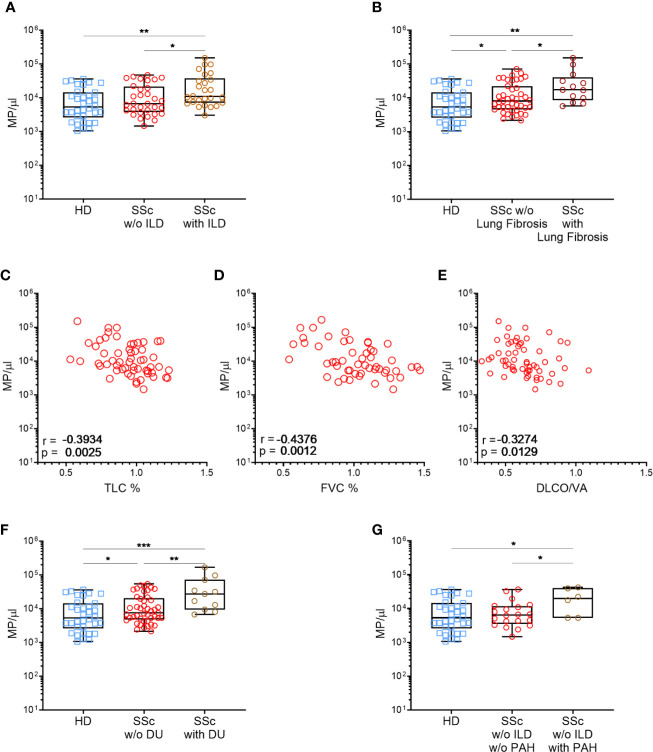
Figure 2.
High MPs concentrations are associated with severe SSc phenotypes. Circulating MPs were compared between HD, patients with and without diffuse interstitial lung disease [Normal = 32, interstitial lung disease = 26; (A)], and lung fibrosis [HD = 37, SSc =43, SSc with lung fibrosis=13; (B)]. The concentration of circulating MPs is compared to the lung function test of SSc patients (SSc=59): TLC (C), FVC (D) and DLCO/VA (E). Circulating MPs were compared between HD, patients with or without vascular injury like digital ulcers [HD = 37, SSc =47, SSc with digital ulcers = 11; (F)] or pulmonary arterial hypertension without interstitial lung disease [HD = 37, SSc = 20, SSc with PAH = 6; (H)]. In (A, B, F, G) symbols represent individual subjects; Box-plots represent the extreme values, the first and third quartiles and the medians. In (C–E), Correlations were determined using Spearman’s test. *p<0.05 by Mann-Whitney (A–C, F–H), **p<0.01 by Mann-Whitney (A–E, G), ***p<0,001 (G). MPs, microparticles; HD, healthy donors; SSc, systemic sclerosis; ILD, interstitial lung disease; TLC, total lung capacity; FVC, forced vital capacity; DLCO/VA, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; DU, active digital ulcers; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension.