Figure 3.
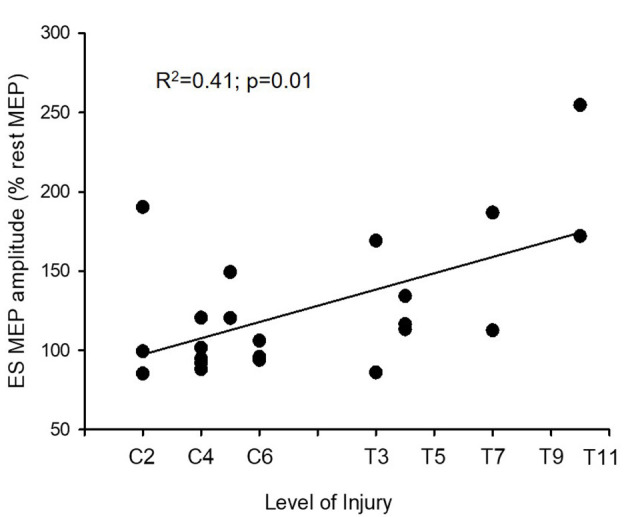
Motor evoked potentials (MEPs) and level of injury. The level of injury correlates with amplitudes of MEP in the erector spinae (ES) muscle during elbow flexion (n = 22). The ordinate shows the size of the ES MEP during the elbow flexion (as a % of the ES MEP obtained at rest). Note that the crossed facilitatory effect of the arm contraction on the trunk muscle is greater in subjects with a more caudal injury, near the recording muscle (the ES muscle at the 12th thoracic vertebral level, T12).
