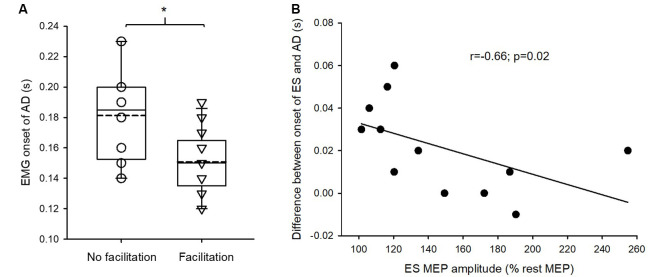
Figure 4.
Electromyography (EMG) of anterior deltoid (AD) and erector spinae (ES) in the rapid shoulder flexion task. (A) The onset of EMG activity in AD is earlier in patients with crossed facilitation (n = 14) than in those without (n = 8), indicating that patients with the crossed facilitation react quicker to a visual cue. Solid lines indicate median values; dotted lines indicate mean values. The box is interquartile range; error bars denote maximum and minimum values. (B) Increased the size of motor evoked potential (MEP) in the ES muscle correlates with the onset of EMG activity in ES concerning AD during the rapid shoulder flexion task in patients with crossed facilitation. This indicates that patients who have preserved crossed facilitation of the trunk muscles show the better function of anticipatory postural adjustments during functional arm movements. *p < 0.05 in comparison between subgroups.