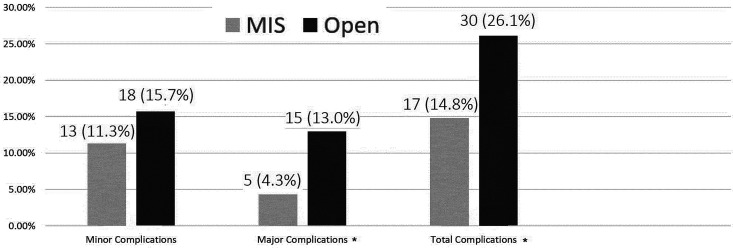
Figure 2.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) versus open postoperative complications, overall analysis (univariate analysis). Minor complications included urinary tract infection (UTI), pneumonia, neurological deterioration to a minor extent, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak that resolved without revision surgery, superficial wound infection, need for postoperative inhalations of steroids and bronchodilators. Major complications included death, score drop on ASIA (American Spinal Injury Association) impairment scale, postoperative revision surgery, deep wound infection, meningitis, operated epidural hematoma, prolonged ventilation. *Statistically significant (P < .005).