-
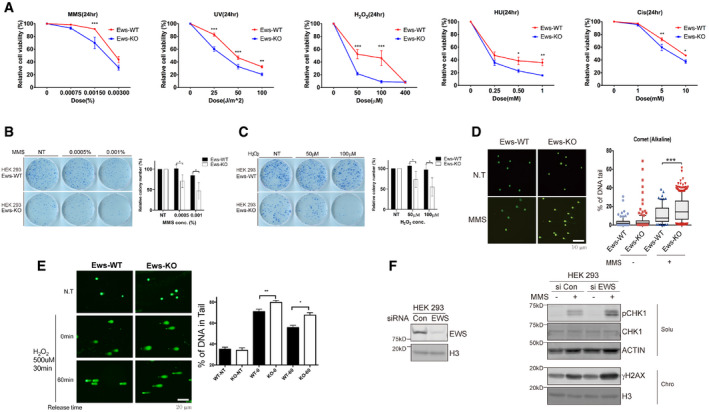
A
Relative cell viability was measured in wild‐type (WT) and Ews‐KO mBA cells after treatment with various DNA‐damaging agents. MMS: Methyl methane sulfonate, H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide, Cis: Cisplatin, UV: Ultraviolet, and HU: Hydroxyurea. Error bars represent as mean ± SEMs, and technical repeats (n = 3). Significance determined by two‐way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
-
B, C
After 10 days of low dose MMS (B) and H2O2 (C) treatment, survived colony were measured using clonogenic assay. Data represented as mean ± SEMs, n > 3. Significance determined by Student's t‐test, two‐tailed, *P < 0.05.
-
D
DNA breaks in wild‐type (Ews‐WT) and Ews‐KO mBA cells were measured using Alkaline Comet assay after MMS treatment (0.0015%, 24 h). Error bars represent as mean ± SEMs, n > 50. Significance determined by ***P < 0.001.
-
E
Alkaline Comet assay were conducted in Ews‐WT and Ews‐KO mBA cells after treatment and release of H2O2. Error bars represent ± SEMs, n > 50. Significance determined by two‐way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
-
F
Upon inactivation of EWS in HEK‐293 cells, expression of DNA damage markers (pCHK1 and γH2AX) were measured using Western blotting after MMS (0.02%, 1 h) treatment.