-
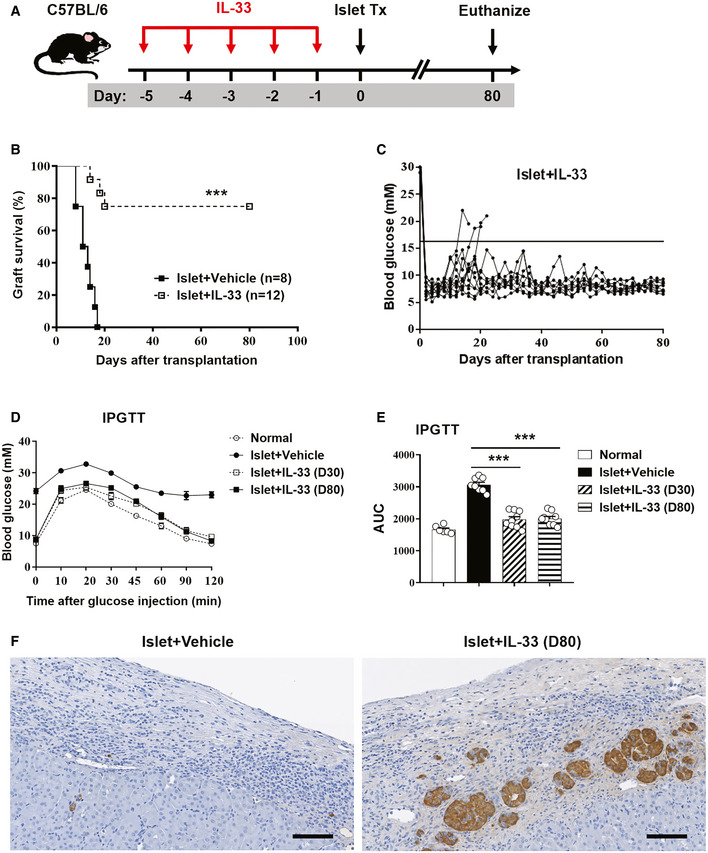
A
Streptozotocin‐induced diabetic C57BL/6 (H2b) mice were treated with mouse recombinant IL‐33 daily for 5 consecutive days before islet transplantation. On day 0, mice were transplanted with BALB/c (H2d) islets. Mice were sacrificed at day 80 post‐islet transplantation or at the day when grafts were considered rejected after two consecutive BGLs > 16 mmol/l (mM) after a period of normoglycemia.
-
B
Islet graft survival of mice receiving vehicle (PBS) or IL‐33 was assessed by monitoring blood glucose and calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method. Cumulative data from two independent experiments are shown. Statistical analysis was performed with a log‐rank test. ***P < 0.001 vs. islet+vehicle.
-
C
Blood glucose level of mice treated with IL‐33 (the horizontal black line indicates a BGL of 16 mmol/l, the threshold for rejection). Each line represents one mouse.
-
D
Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) was assessed in normal mice, islet transplant mice receiving vehicle (on the day when grafts were considered rejected), and islet transplant mice treated with IL‐33 (at day 30 and day 80 post‐islet transplantation). Data shown are the mean ± SEM (n = 6–9 per group).
-
E
Area under the curve (AUC) for IPGTT was assessed. Data shown are the mean ± SEM (n = 6–9 per group), and a one‐way ANOVA was performed, ***P < 0.001.
-
F
Representative immunohistochemical staining for insulin in graft samples from mice receiving vehicle or IL‐33. Scale bar = 100 μm.