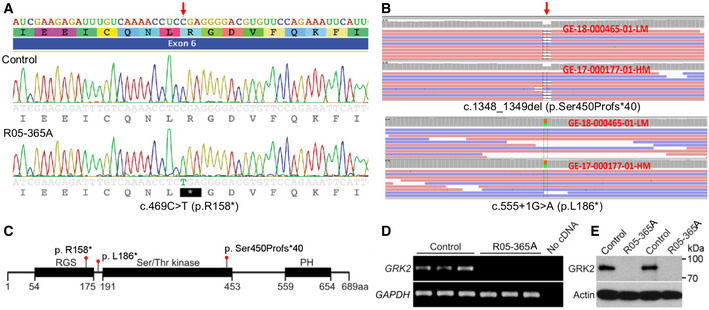
Figure 2. Homozygosity and compound heterozygosity for null mutations in GRK2 in ATD .
-
ASanger sequence trace showing homozygosity for the c.469C>T mutation, predicting a stop codon in exon 6 of GRK2 (arrow).
-
BExome analysis showing the biallelic changes c. 1348_1349del and c.555 +1G>A. Red arrow points to the place of mutation. Orange and green boxes indicate the reference nucleotide and its substitution, respectively.
-
CDomain composition of GRK2 and the corresponding location of the mutations (RGS, regulator of G protein signaling domain; PH, pleckstrin homology domain).
-
DExpression of GRK2 as measured by RT–PCR in three replicates each of control and R05‐365A fibroblasts, demonstrating absence of GRK2 transcript in ATD cells. GAPDH served as a positive control.
-
ETwo control and ATD fibroblast samples were immunoblotted for GRK2. Note the absence of GRK2 protein in the ATD cells. Actin served as a loading control. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments.
Source data are available online for this figure.
