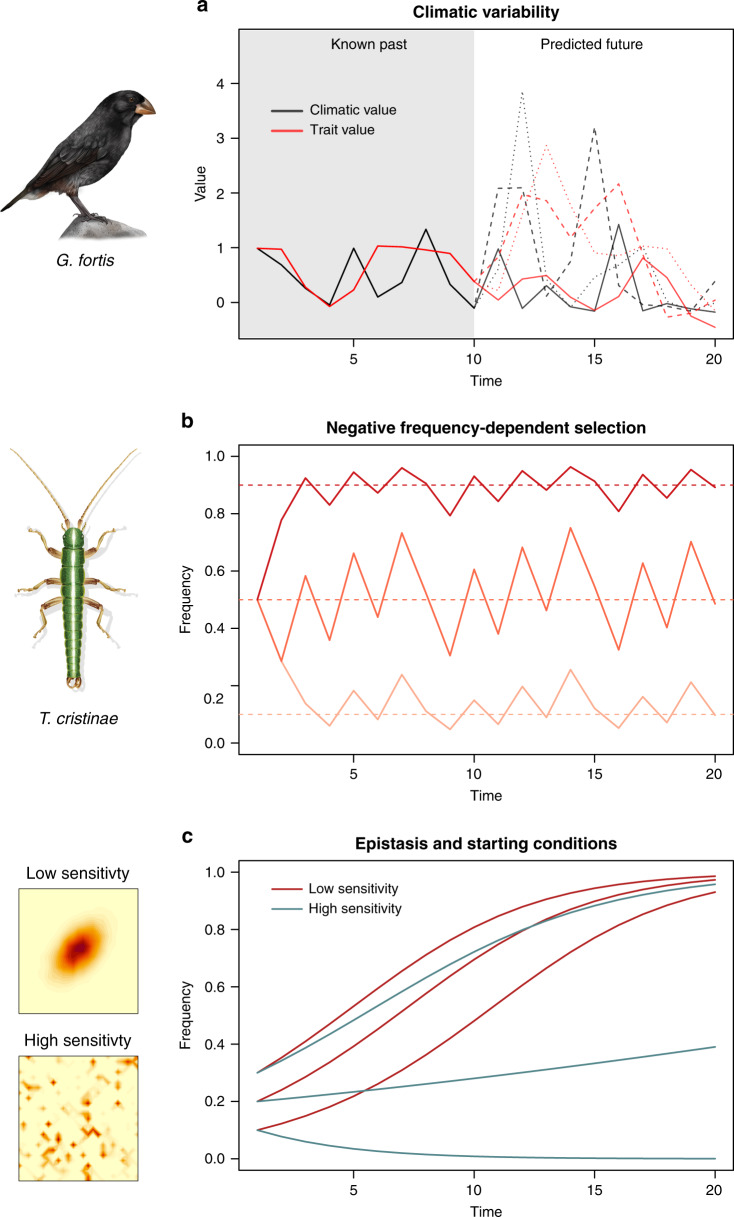
Fig. 3. Hypothetical examples of how variation in different factors can limit the predictability of evolution driven by deterministic natural selection.
This figure is motivated by empirical systems, but does not depict real data. a Uncertainty in climatic variability can limit the predictability of evolution for traits affected by environment-dependent fluctuating selection, such as beak size in G. fortis. Here black lines denote observed (left half) or predicted (right half) climatic values, and red lines denote observed (left half) or predicted (right half) trait values. Multiple possible predictions are shown. b Uncertainty in the form of the selection function can limit the predictability of evolution by negative frequency-dependent selection, as is observed for color pattern in T. cristinae stick insects. Possible evolutionary trajectories given three different selection functions (different colored lines) are shown here. c Predictability can also be limited by sensitivity to initial conditions, as occurs on rugged fitness landscapes with considerable epistasis. Two hypothetical fitness landscapes with low (top) and high (bottom) epistasis, and thus sensitivity to initial conditions, are shown (left side; the axes represent genotypes for different loci). Hypothetical evolutionary trajectories from different starting conditions are shown on the right (colored lines). High epistasis promotes different outcomes dependent on initial conditions. Finch and stick insect drawings courtesy of R. Ribas.