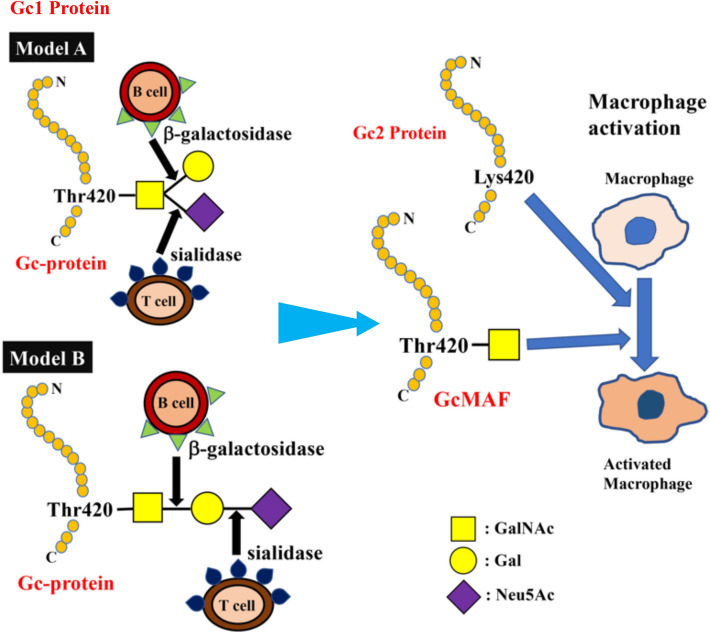
Figure 1.
Structure of Gc protein and its conversion to GcMAF. Yamamoto et al. proposed (Model A) for the structure of DBP/Gc1F protein and its conversion to GcMAF25. In this model, GalNAc is covalently bound to Thr420 of the Gc1F protein and galactose and sialic acid are bound to GalNAc in a Y-branched arrangement. Therefore, removal of galactose and sialic acid exposes the GalNAc moiety and leads to the formation of activated GcMAF. However, Ravnsborg et al. recently proposed a linear model (Model B) based on mass spectrometry findings23. In this model, the three sugar moieties attached to threonine 420 are arranged in a linear fashion with GalNAc covalently bound to threonine, and galactose and sialic acid attached to the GalNAc in this order. Non-glycosylated Gc2 is also illustrated based on current mass spectrometry findings.