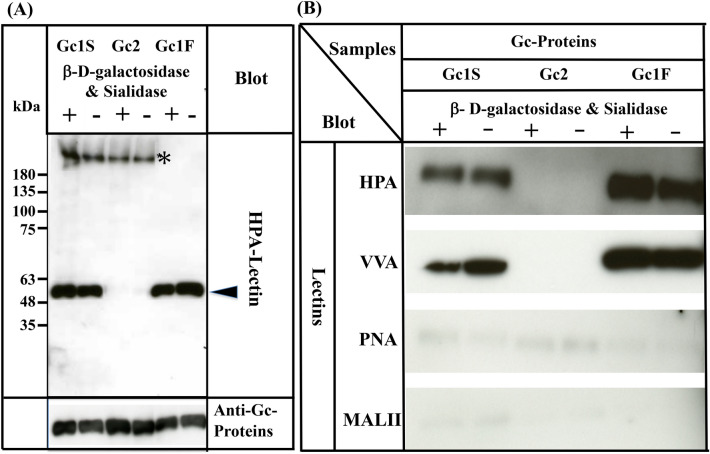
Figure 4.
Characterization of Gc1S, Gc2 and Gc1F synthesized by ExpiCHO-S cells in serum-free suspension culture. Gc1S and Gc2 were synthesized by ExpiCHO-S cells transfected with pcDNA3.4-TOPOGc1S-His or pcDNA3.4-TOPOGc2-His (Supplementary Fig. 1) in serum-free suspension culture. Gc1S and Gc2 were purified by His Trap HP (Ni2+ pre-charged) column chromatography and desalted by dialysis against 50 mM sodium phosphate pH 7.0 (desalted fraction). Sugar moieties of the desalted fraction alone (−) and after treatment with β-d-galactosidase and sialidase (+) were analyzed by blotting with biotin-conjugated HPA-lectin (arrowhead). Purified Gc1F was analyzed as a control. Gc1S, Gc2 and Gc1F reacted with anti-Gc antibody (lower column). Extra bands indicated by * were unknown HPA-lectin reactive proteins that became undetectable after vitamin D affinity column chromatography (see lanes 1F+, 1F−). (B) Gc1F, Gc1S and Gc2 synthesized by ExpiCHO-S cells in serum-free suspension culture were purified by His Trap HP (Ni2+ pre-charged) column chromatography and Vitamin D affinity column chromatography, and then desalted by dialysis against 50 mM sodium phosphate pH 7.0 (desalted fraction). Sugar moieties of the desalted fraction without treatment (−) and after treatment with β-d-galactosidase and sialidase (+) were analyzed by blotting with HPA, VVA, PNA, or MALII lectins as indicated. Full-length blots are included in a Supplementary Fig. 4.