Figure 1.
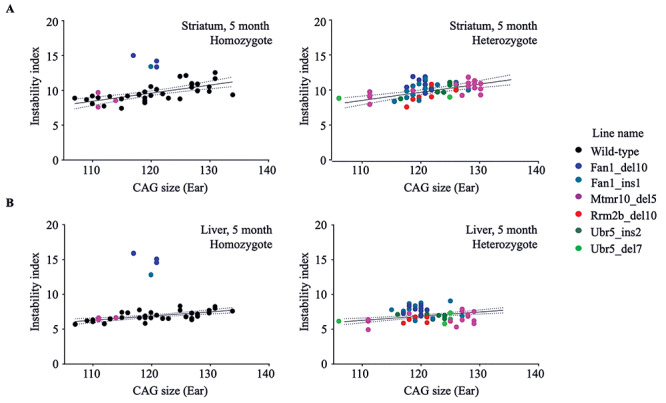
Fan1_del10 and Fan1_ins1 mutations enhance somatic instability of the HdhQ111/+ CAG repeat. The instability index (Y-axis), a quantitative measure of CAG repeat instability, calculated from ABI3730XL trace profiles (Methods) of PCR amplification products generated with DNA isolated from striatum (top panels) and liver (bottom panels) of genotyped progeny of matings between HdhQ111/+ and Fan1, Mtmr10, Rrm2b or Ubr5 mutant parental mice, is plotted against the size of the CAG repeat measured in the stable ear tissue of the same mouse at 3 weeks of age (X-axis). The instability index of mutant Fan1_del10 homozygote (n = 3), Fan1_ins1 homozygote (n = 1) and Mtmr10_del5 homozygote (n = 3) mice (left panel) and mutant Fan1_del10 heterozygote (n = 8), Fan1_ins1 heterozygote (n = 12), Mtmr10_del5 heterozygote (n = 16), Rrm2b_del10 heterozygote (n = 7), Ubr5_ins2 heterozygote (n = 7), Ubr5_del7 heterozygote (n = 5) mice (right panel) is shown relative to the instability index of wild-type littermates (n = 34). The regression trend line (solid line) and 95% confidence interval (dotted lines) illustrate the instability for a given inherited HdhQ111/+ CAG size in the absence of modifier gene mutation at 5 months of age.
