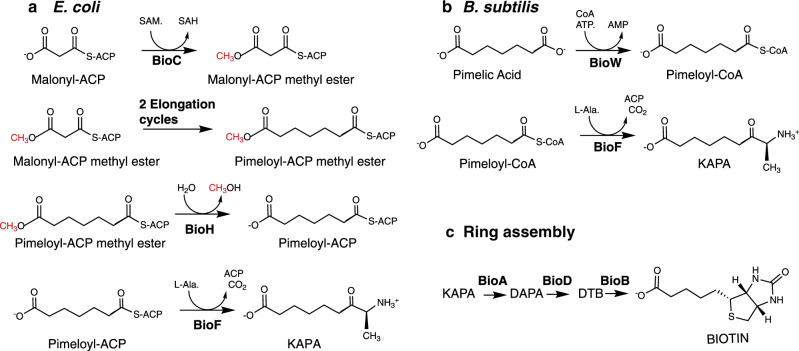
Fig. 1. The known pathways of pimeloyl moiety synthesis.
a In E. coli and (as inferred from genome analyses) many other bacteria, malonyl-ACP methyl ester replaces the usual acetyl primer of fatty-acid synthesis. After two cycles of chain elongation the methyl group is removed by BioH to give the BioF substrate, pimeloyl-ACP. (Red letters denote the methyl group donated by S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM) and subsequently released as methanol. b In B. subtilis the pimelate chain is also assembled by fatty-acid synthesis, but unlike E. coli, the pathway proceeds through a free pimelic acid intermediate that requires activation by BioW. c Schematic of the late steps in biotin synthesis. Systematic chemical nomenclature for KAPA is 7-keto-8-aminopelargomic acid whereas DAPA is 7,8-diaminononanoic acid. DTB is dethiobiotin.