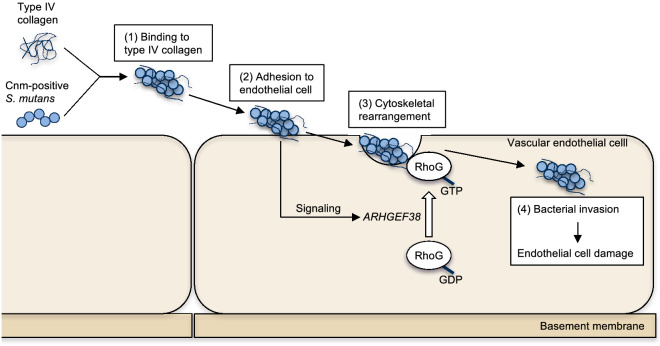
Figure 7.
Proposed model of the interaction between Cnm-positive S. mutans and vascular endothelial cells. Cnm-positive S. mutans strains adhere to type IV collagen in the serum, and (2) then adhere to vascular endothelial cell surfaces. (3) The binding of bacteria activates ARHGEF38 in the endothelial cells, leading to GDP–GTP exchange and the activation of Rho family G proteins, cytoskeletal rearrangement, and bacterial internalization. (4) Invasion by Cnm-positive S. mutans induces vascular endothelial cell damage.