FIGURE 1.
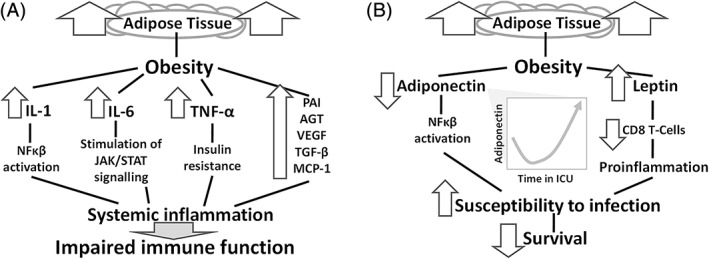
A, Cytokines and inflammation in subjects with obesity. Release of inflammatory molecules represents the cornerstone of obesity‐induced inflammation. NF‐κB: Nuclear Factor kappa‐light chain‐enhancer of activated B‐cells. B, Adipose tissue and adipokines in subjects with obesity. Healthy adipose tissue secretes less leptin and more adiponectin, preventing inflammation. In obesity, this is inversed and reduced levels of the anti‐inflammatory adiponectin favour resistance to leptin and subsequent susceptibility to infections. This is notable for lung infections and critical illness that requires treatment in an intensive care unit (ICU). AGT, angiotensinogen; MCP‐1, monocyte chemoattractive protein‐1; PAI‐1, plasminogen activator inhibitor‐1; TGF‐β, transforming growth factor‐ β; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor
