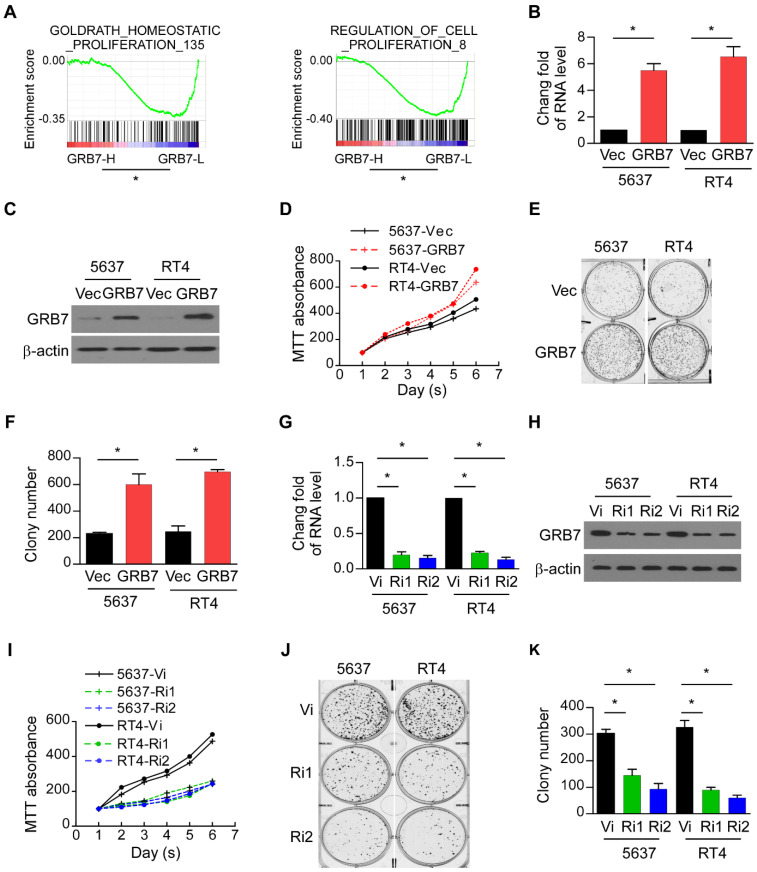
Figure 2.
GRB7 regulates the proliferation of bladder cancer cells. A. GSEA plots demonstrated that the expression of GRB7 in bladder cancer is positively correlated with cell proliferation. *P < 0.05. B. RT-qPCR analysis showed that 5637 and RT4 cells were successfully and constantly transfected with GRB7 plasmids to overexpress the expression of GRB7. C. Western blot analysis showed that 5637 and RT4 cells were successfully and constantly transfected with GRB7 plasmids to overexpress the expression of GRB7. D. MTT assays showed that overexpression of exogenous GRB7 significantly increased the growth rate of 5637 and RT4 cells. E. A representative image from the colony formation assay showed that overexpression of exogenous GRB7 significantly increased the mean colony number in the colony formation assay. F. The mean count of the colony number in the colony formation assay. G. RT-qPCR analysis showed that 5637 and RT4 cells were successfully and constantly transfected with GRB7 plasmids to overexpress the expression of GRB7. H. Western blot analysis showed that the endogenous GRB7 were successfully silenced. I. MTT assays showed that silencing endogenous GRB7 significantly reduced the growth rate of 5637 and RT4 cells. J. A representative image from the colony formation assay showed that silencing endogenous GRB7 significantly reduced the mean colony number in the colony formation assay. K. The mean count of the colony number in the colony formation assay. *P < 0.05.