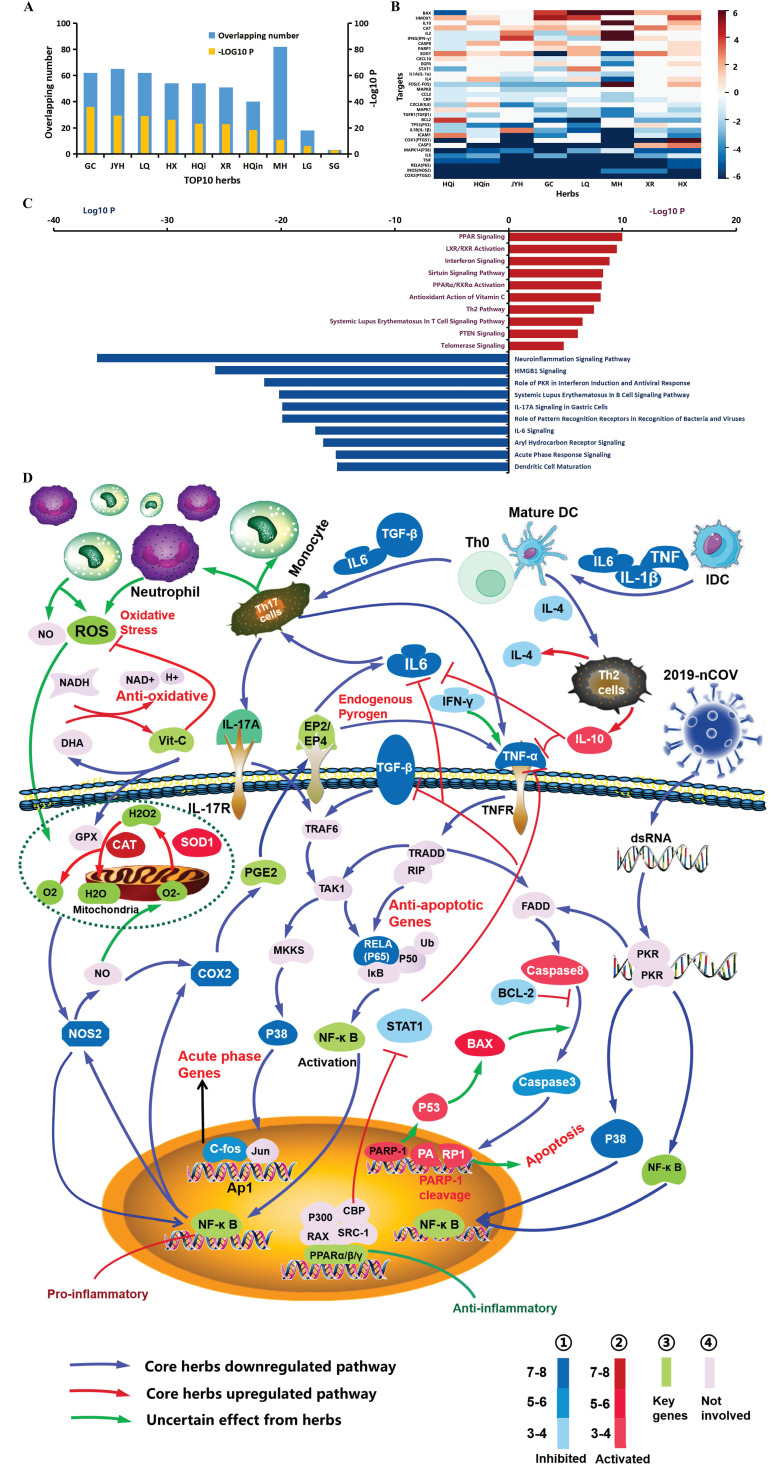
Figure 3.
Functional analysis and potential mechanisms of the top commonly used herbs. (A) Intersection of the top 10 herb targets with COVID-19 targets. All the target analyses were constrained within the TCMSP database. The number of overlapping targets is shown in blue, while the significance (-Log10 P) of the coherent intersection is shown in orange. The most commonly used herbs are represented by acronyms. GC: licorice glycoside, Gan Cao; JYH: Flos Lonicerae, Jin Yin Hua; LQ: Fructus Forsythiae, Lian Qiao; HX: Herba Agastaches, Huo Xiang; HQi: Radix Astragali seu Hedysari, Huang Qi; XR: Semen Armenia cae Amarum, Xing Ren; HQin: Radix Scutellariae, Huang Qin; MH: Herba Ephedrae, Ma Huang; LG: Rhizoma Phragmitis, Lu Gen; SG: Gypsum Fibrosum, Shi Gao. (B) Heatmap of herb targets. The depth of color, as indicated in the number bar, represents the frequency of a target gene with compounds from a corresponding herb, the so-called target count (TC). A TC of more than 6, e.g., 112 TC of COX2 (PTGS2) to GC, were unified (the original data are shown in Table S5). Red represents positive regulation, blue represents negative regulation, and white represents no change, multiregulation or lack of reports, which were determined from the literature (Table S6). (C) Pathway analysis with directions of herb targets. Ten up- and downregulated pathways by 8 herbs, according to Log10 P using IPA, are shown. The red bar indicates activation, while the blue bar shows inhibition. The crucial identified pathways are shown in the diagram (Fig. 3D), including the activated pathways (“PPAR signaling”, “interferon signaling”, “PPARα/RXRα activation”, “antioxidant action of vitamin C” and “Th2 pathway”) and the inhibited pathways (“pole of PKR in interferon induction and antiviral response”, “IL-17A signaling”, “IL6 signaling”, “acute phase response signaling” and “dendritic cell maturation”). (D) Pathway diagram presenting the potential molecular mechanisms by which the core herbs impact COVID-19. The key targets modulated by both herbs and COVID-19 were classified into 3 categories, according to the results of Fig. 3B: inhibited (blue tones), activated (red tones) and not involved in herbs (discussed key target genes are presented in green, while the general in purple). The depth of color varies as the amounts of same regulation from 8 herbs. Pathways were divided into three categories: downregulated with herbs in blue, upregulated with red and uncertain with green.