Fig. 3.
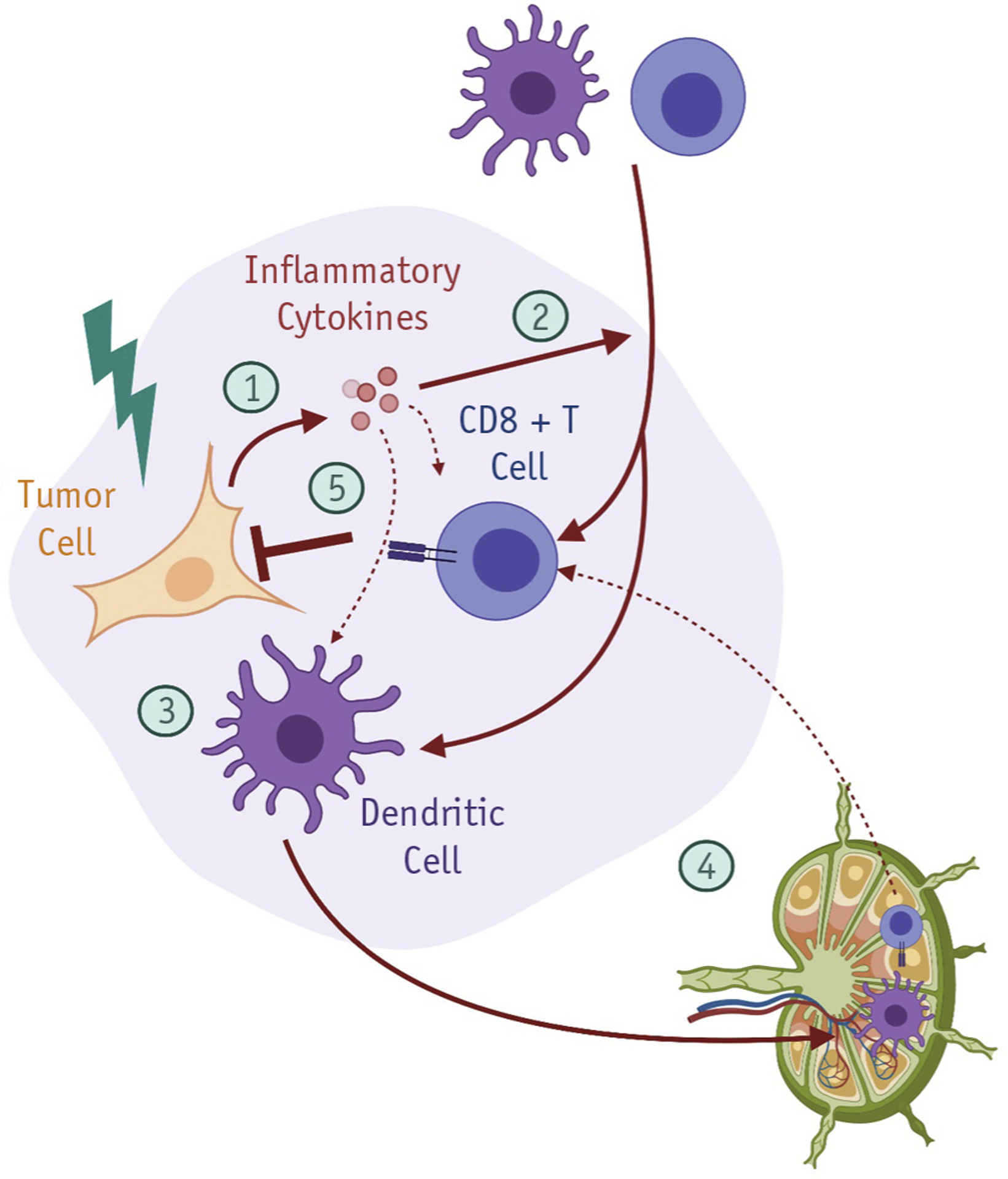
RT modulation of antitumor immune responses. RT exerts pleiotropic immunomodulatory effects on the tumor microenvironment. (1) RT-induced DNA damage in tumor cells stimulates innate immune signaling, in part through expression of type I interferon genes. (2) RT-induced chemokines promote infiltration of circulating lymphocytes and innate immune cells into the tumor microenvironment. (3) RT/IO can stimulate tumor cell phagocytosis by professional APCs, and (4) cross-presentation of tumor neoantigens in tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLNs). (5) RT/IO can facilitate activation of primed tumor-reactive T cells to eradicate tumor cells at both the primary site and distant sites. Figure created with Biorender.com. Abbreviations: APC = antigen-presenting cells; RT = radiation therapy; RT/IO = radiation therapy/immunotherapy; TDLN = tumor-draining lymph nodes.
