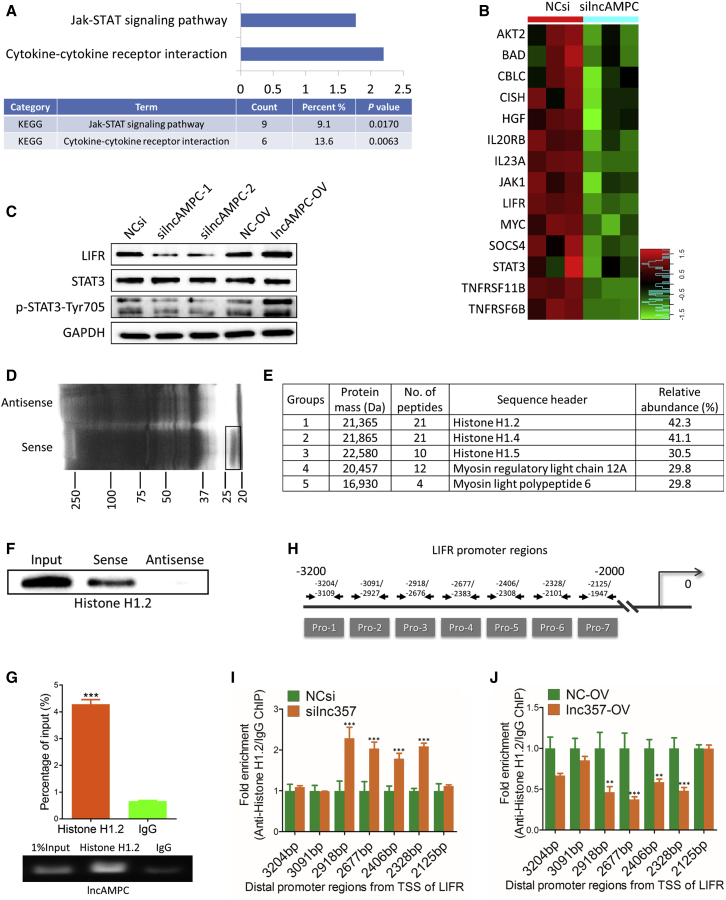
Figure 5.
lncAMPC Enhances the Transcription of LIFR by Decoying Histone H1.2 Away from the Upstream Sequence of LIFR Gene
(A) KEGG pathway analysis of genes affected by lncAMPC knockdown in PC-3 from microarray data. (B) Heatmap showing the expression data of genes involved in cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction and Jak-STAT signaling pathway. (C) Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins in PC-3 transfected with NCsi, silncAMPC-1, silncAMPC-2, NC-OV, or lncAMPC-OV (n = 3). (D) RNA pull-down precipitates of lncAMPC-associated proteins were separated via SDS-PAGE and visualized using silver staining (n = 3). The black frame indicates the section of the gel cut out for mass spectrometry analysis. (E) Mass spectrometry analysis of the proteins specifically pulled down by lncAMPC. (F) Western blot analysis of histone H1.2 in the RNA pull-down precipitates retrieved with biotin-labeled lncAMPC or antisense RNA from the lysates of PC-3 cells (n = 3). (G) RIP assay of the enrichment of histone H1.2 with lncAMPC relative to IgG in the lysates of PC-3 cells (n = 3). (H) The 7 pairs of primers designed to cover the 3,200 bp–2,000 bp distal promoter regions from the transcription start site of LIFR. (I and J) Anti-histone H1.2 ChIP assay followed by quantitative real-time PCR to detect the binding ability of histone H1.2 to LIFR distal promoter regions in PC-3 cells transfected with NCsi or silncAMPC-2 (I) and NC-OV or lncAMPC-OV (J) (n = 3). Results are presented as mean ± SD; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.