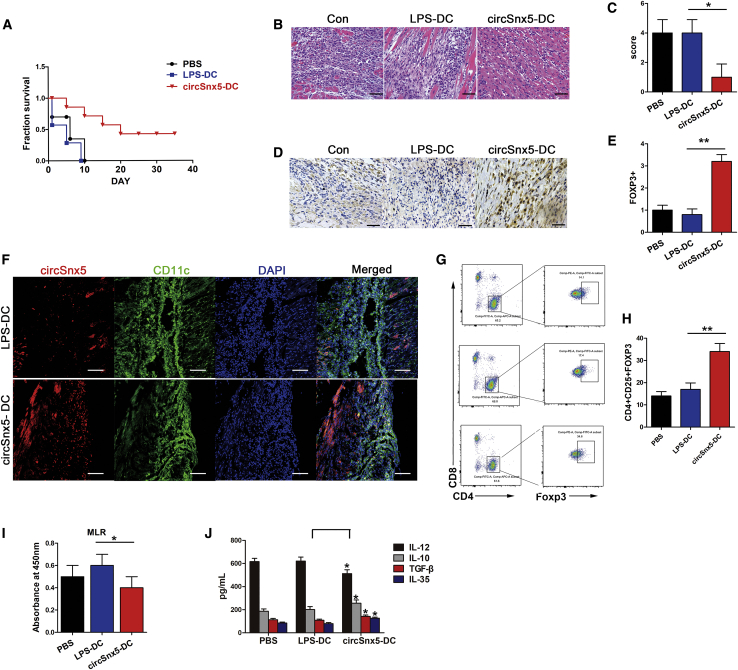
Figure 6.
Transfer of circSnx5-Overexpressing DCs Induced Treg Expansion and Protects Acute Rejection after Cardiac Transplantation
(A) Graft survival times of recipients is shown. The survival times in the groups were compared using Mann-Whitney U testing. (B and C) Histology typical of the three groups of mice. (B) Tissue sections were stained with H&E. The images are representative of several individuals from each group (n = 6 biological replicates). Scale bars, 200 μm. (C) Quantitative evaluation of myocardial inflammation. (D and E) Immunohistochemical analyses (D) were performed using anti-Foxp3 primary antibodies to detect Tregs. (E) The percentages of Foxp3+ cells were enumerated. The images are representative of several individuals from each group (n = 6 biological replicates). Scale bars, 50 μm. (F) Immunohistochemistry detection of the DC markers CD11c and circSnx5 in mouse transplanted tissues. The images are representative of several individuals from each group (n = 6 biological replicates). Scale bars, 20 μm. (G and H) Flow cytometry was performed to detect expression of Tregs (CD4+, CD25+, and Foxp3+) of spleens from recipients with circSnx5 overload compared with control mice (G), and are shown as percentages (H). (n = 6 biological replicates). (I) Splenic T cells were separated from recipient mice at day 7 post-transplantation. The proliferating activity of splenic T cells was assessed by BrdU-ELISA. (n = 6 biological replicates). (J) IL-10, IL-12, TGF-β, and IL-35 levels detected by ELISA in the plasma of recipient mice 14 days after heart transplantation. (n = 6 biological replicates). Data are shown as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, by Student’s t test.