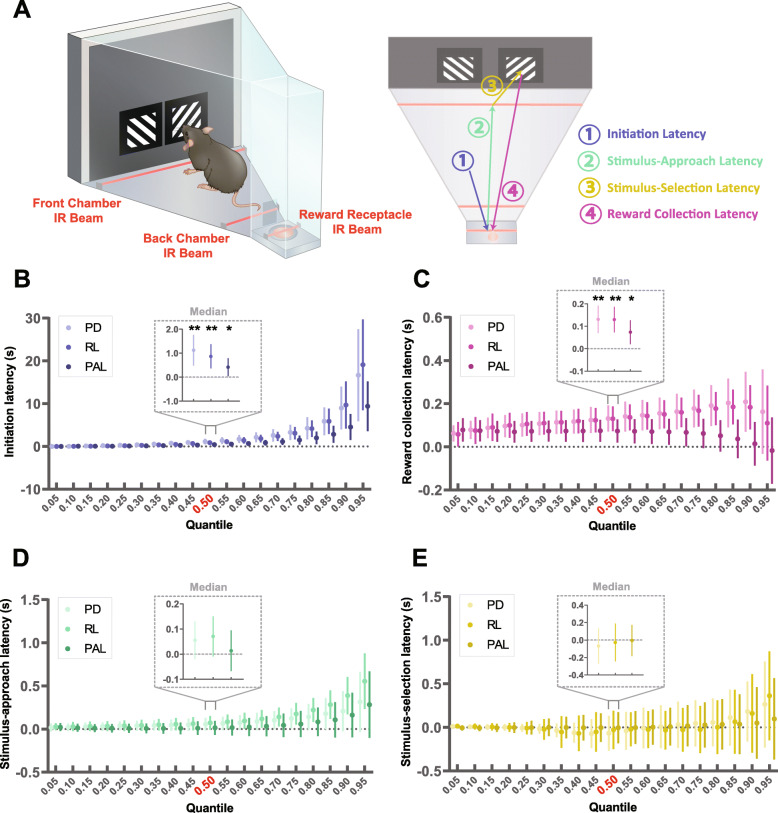
Fig. 3.
Nlgn1−/− take longer to perform instrumental actions for rewards. a Infrared (IR) beams located within the chambers at the front, back, and reward receptacle allow the dissection of multiple reaction times (initiation latency; stimulus-approach and stimulus-selection latency; reward collection latency, see the “Methods” section and Additional file 1: Fig. S4). Nlgn1−/− mice took longer to b initiate trials, c collect rewards, and d approach the touchscreen (stimulus-approach latency) but not e stimulus-selection across tasks (effect of genotype > 0). b–e Latency differences between Nlgn1−/− and WT mice estimated by quantile regression from the 0.05th to 0.95th quantile at steps of 0.05, with insets highlighting median quantile values. Pairwise visual discrimination (PD), reversal learning (RL), object-location paired associate learning (PAL), data arranged in order of task training. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, quantile regression values represent estimated latency difference between Nlgn1−/− and WT mice ± 95% CI