Figure 7a.
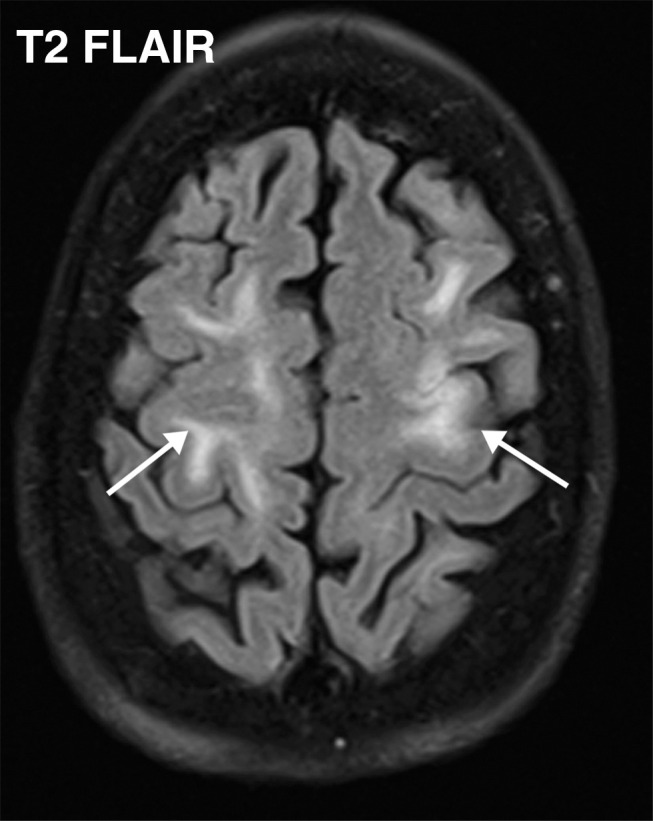
Watershed infarcts and cardioembolic infarcts in a 55-year-old woman with COVID-19 who presented with left gaze deviation. (a) Initial axial T2-weighted (T2) FLAIR brain MR image shows hyperintense signal abnormality (arrows), predominantly within the high frontal and parietal subcortical white matter bilaterally. (b) Repeat axial T2-weighted (T2) FLAIR MR image obtained 3 days later shows interval development of a linearly oriented pattern of signal abnormality (arrows) within the centrum semiovale bilaterally, greater on the left than on the right. (c, d) Axial diffusion-weighted (DWI) (c) and ADC (d) brain MR images show restricted diffusion in the corresponding areas of abnormality (arrows), indicative of watershed infarcts. (e, f) Axial diffusion-weighted (DWI) (e) and ADC (f) brain MR images show restricted diffusion involving the bilateral occipital lobes (arrows), indicative of additional foci of acute infarct.
