Figure 4. Peptide constituents of PKA-associated modules.
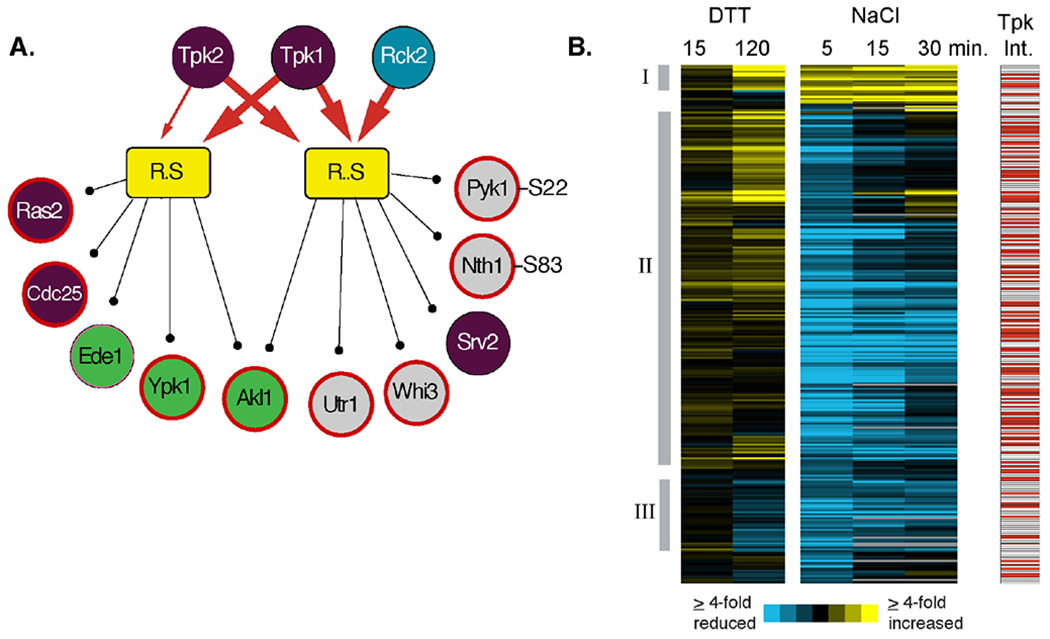
(A) Two modules of late-responding phosphopeptides with increased phosphorylation after DTT treatment and for which PKA subunits were identified as shared interactors are shown as in Figure 2. Note, in each case, we combined one module that was independent and one dependent on Mkk1/2 but for which shared interactors and phospho-motifs were otherwise identical. Heavy red arrows connect shared interactors identified at an FDR of 0.02, and light red arrows reflect shared interactors identified at FDR of 0.05. Only a subset of module constituents are shown, including regulators in the RAS/PKA pathway (purple circles), proteins involved in endocytosis (green circles), and known PKA protein targets 72 and phosphorylation sites (bold red outline) 70. (B) Hierarchical clustering of 268 peptides contained within PKA-connected modules in response to either 2.5 mM DTT or 0.7M NaCl treatment at the denoted times. Each row represents a different peptide, each column represents a different time point, and colorized data represent the log2(fold change) in phosphorylation state according to the key. The response to DTT and 5 min post NaCl treatment represent the average of biological triplicates. Red boxes to the right represent proteins that physically interact with one or more PKA catalytic subunit. Manually identified clusters discussed in the text are indicated.
