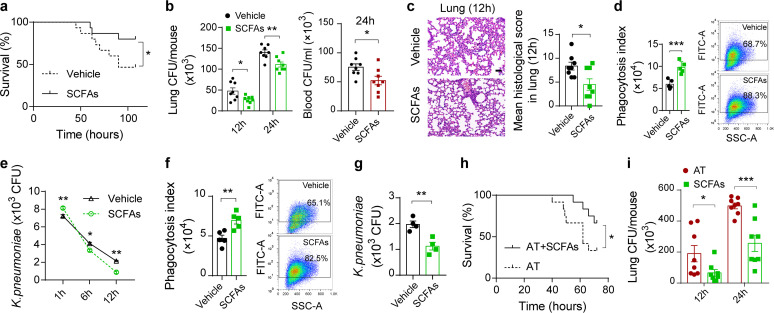
FIG 3.
SCFAs promote inflammatory responses during K. pneumoniae-induced sepsis. (a) Survival rates of SCFA-treated mice and untreated controls postinfection with 1 × 105 CFU of K. pneumoniae. (b) Lung and blood bacterial burdens in SCFA-treated mice and untreated controls 12 h and 24 h after K. pneumoniae infection. (c) Representative H&E staining and quantification of pathological scores of lung sections from SCFA-treated mice and untreated controls 12 h after K. pneumoniae infection. Scale bars, 50 μm. (d) Phagocytic capacity of isolated alveolar macrophages from SCFA-treated mice and untreated controls. (e) Bacterial loads of isolated alveolar macrophages from SCFA-treated mice and untreated controls. (f, g) Phagocytosis (f) and clearance (g) of SCFA-treated differentiated THP-1 cells and untreated controls after K. pneumoniae infection. (h) Survival rates of antibiotic-treated mice treated with SCFAs or vehicle. (i) Pulmonary bacterial burdens in antibiotic-treated mice treated with SCFAs or vehicle. The group size was 8 to 12 mice. Data are from three independent experiments (b, d to g, i) or one experiment representative of three independent experiments (a, c, h) (means ± SEM). The P values were determined using a log rank (Mantel-Cox) test (a, h) or two-tailed Student t tests (b to g, i). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.