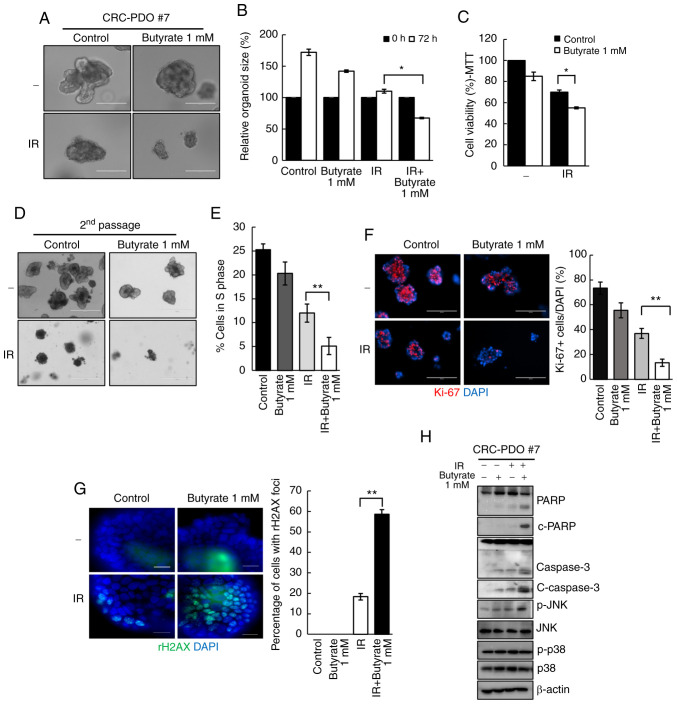
Figure 2.
Butyrate enhances radiosensitivity in CRC-PDOs. (A) Morphology and (B) organoid size (n=3) of CRC-PDO #7 irradiated thrice with 5 Gy with or without butyrate. Scale bar, 200 µm. (C) MTT cell viability assay of organoids described in A (n=3). (D) Image of organoids after the second passage. Scale bar, 400 µm. (E) Percentage of CRC-PDO in S phase (n=3). (F) Left: Fluorescence microscopy images of organoids irradiated thrice with 5 Gy with or without butyrate. Blue, DAPI; red, Ki-67. Scale bar, 200 µm. Right: Statistical analysis representing Ki-67-positive cells per DAPI staining cells (n=3). (G) Fluorescence microscopy images showing γ-H2AX foci. Blue, DAPI; green, γ-H2AX. Right: Statistical analysis representing γ-H2AX foci (n=3). (H) Expression levels of PARP, c-PARP, caspase 3, c-caspase 3, p-JNK, JNK, p-p38 and p38 in the CRC-PDO. β-actin served as a loading control. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. CRC, colorectal cancer; PDO, patient-derived organoid; PARP, poly-ADP-ribose polymerase; c-, cleaved; p-, phosphorylated; IR, irradiation.