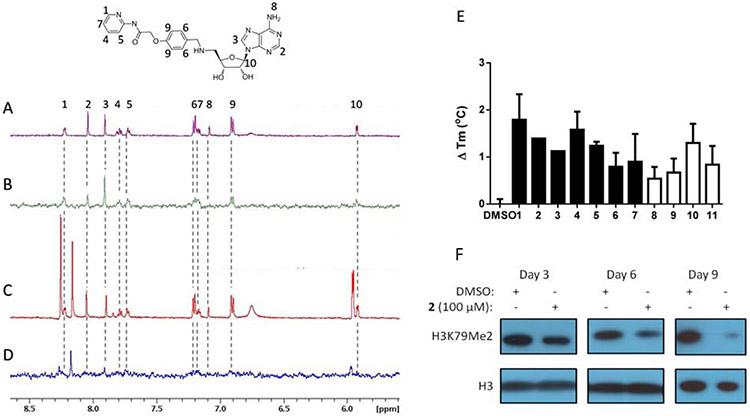
Figure 3. DOT1L inhibitors bind to the SAM binding site.
NMR spectra of 200 μM 2 in the presence of 5 μM GST-DOT1L. (A) 1H NMR of 2. Compound protons numbered according to corresponding 1H NMR signal. (B) STD NMR of 2 demonstrates binding to DOT1L. (C) 1H NMR with addition of 2 mM SAH. Additional peaks in spectra that do not correspond to 2 are from SAH. (D) STD NMR with addition of 2 mM SAH. Loss of STD NMR signal from 2 indicates that SAH competes with 2 for binding to the SAM binding site. (E) Thermal stability shift assay of 1μM GST-DOT1L in the presence of DMSO or 100 μM adenosine based DOT1L inhibitors (filled bars) or 200 μM non-adenosine DOT1L inhibitors (empty bars) showing increased melting temperature in the presence of compounds indicating binding to DOT1L. (F) 2 inhibits cellular H3K79 dimethylation in MLL-AF9 murine model cells over the time course of 3, 6 and 9 days.