Table 4.
Predictors of 6-Month Post-Concussive Syndrome in 277 Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
| Predictors | Univariable (ß, p value) | Multivariable (ß, p value) | LASSO shrinkage (ß) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (/10y) | 0.50 (p = 0.16) | 0.58 (p = 0.08) | 0.53 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 1.18 (p = 0.37) | 1.68 (p = 0.19) | 0.74 |
| Years of education (/y) | −0.94 (p < 0.01) | −0.84 (p < 0.01) | −0.79 |
| Pre-injury seizures* (yes vs. no) | 4.30 (p = 0.03) | 0.91 (p = 0.63) | - |
| Pre-injury migraine and headache (yes vs. no) | 6.95 (p < 0.01) | 3.30 (p = 0.06) | 2.07 |
| Pre-injury psychiatric disorders** (yes vs. no) | 6.28 (p < 0.01) | 4.15 (p < 0.01) | 3.73 |
| Prior TBI (yes vs. no) | 5.11 (p < 0.01) | 4.34 (p < 0.01) | 3.71 |
| BAL | |||
| -High BAL vs. low/unmeasured | −0.19 (p = 0.92) | −0.49 (p = 0.80) | - |
| -Unmeasured BAL vs. high/low | −0.70 (p = 0.61) | −0.80 (p = 0.54) | - |
| GCS 13 or 14 vs. GCS 15 | 1.07 (p = 0.46) | 0.62 (p = 0.66) | - |
| CT abnormalities*** (yes vs. no) | −2.17 (p = 0.09) | −0.31 (p = 0.82) | - |
| PTA | |||
| - yes vs. no/unknown | −0.47 (p = 0.87) | 0.06 (p = 0.98) | - |
| - no vs. yes/unknown | −0.53 (p = 0.86) | −1.36 (p = 0.64) | −0.47 |
| LOC | |||
| - yes vs. no/unknown | −0.94 (p = 0.70) | −1.02 (p = 0.66) | - |
| - no vs. yes/unknown | −2.65 (p = 0.31) | −2.01 (p = 0.43) | −0.38 |
| Extracranial AIS ≥3 in at least one body region (yes vs. no) | −1.20 (p = 0.51) | −1.09 (p = 0.52) | - |
| R2 | 0.23 | 0.21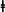
|
|
Unstandardized ß's and p values are shown for all analyses. The multivariable model is based on all candidate predictors in the table.
The expected 6-month Rivermead Post Concussion Symptoms Questionnaire (RPQ) score can be estimated with the following formula: 6-month RPQ = 14.45 + (0.05*Age) + (−0.79*Years of education) + (0.74*female gender) + (2.07*pre-injury migraine or headache) + (3.73*pre-injury psychiatric disorder) + (3.71*prior TBI) + (−0.47* no PTA) + (−0.38*no LOC).
R2 decreased to 0.14 after bootstrap validation with 100 samples.
Includes seizures and epilepsy.
Includes anxiety, depression, sleeping disorders, and bipolar disorder.
Includes epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, contusion, intracerebral hemorrhage, intraventricular hemorrhage, diffuse axonal injury, brain swelling, midline shift, cistern compression, fourth ventricle shift, and third ventricle shift.
LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; TBI, traumatic brain injury; BAL, blood alcohol level; GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale; CT, computed tomography; PTA, posttraumatic amnesia; LOC, loss of consciousness; AIS, Abbreviated Injury Scale.
