Fig. 1.
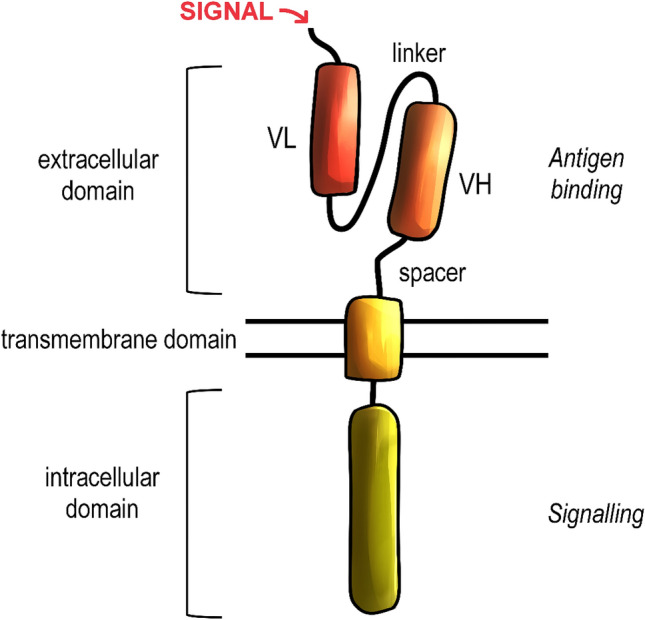
General structure of the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). CARs consist of an extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular domains. The extracellular domain is responsible for antigen binding and it includes the single-chain variable fragment, derived from the antibody domains, precisely variable heavy (VH) and light (VL). The domains are connected together via linker and anchored in the transmembrane domain by a spacer. The transmembrane domain is responsible for the stabilization of CAR. The intracellular domains are derived from the T-cell receptor and are responsible for inducing the cell response after the antigen recognition
