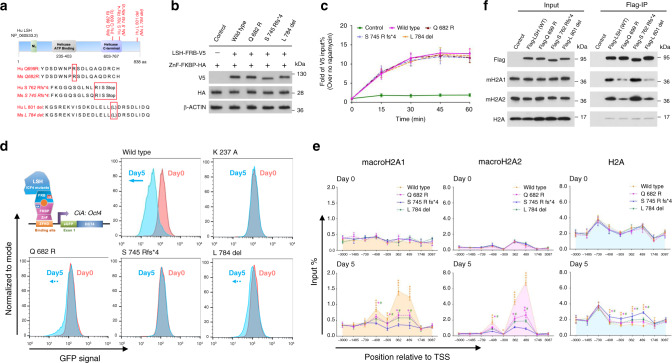
Fig. 6. ICF4 derived LSH mutations fail to induce transcriptional repression and macroH2A deposition.
a Schematic representation of ICF4 associated human LSH mutations (red box) and alignment with murine LSH. b Western blot analysis to confirm the expression of three LSH-FRB-V5 mutant proteins and ZnF-FKBP-HA protein in ICF4 associated LSH CIP system compared to that in wild-type LSH CIP system using V5 and HA antibodies. Cells lacking LSH-FRB-V5 fusion protein expression served as controls. c ChIP-qPCR analysis to determine the recruitment of ICF4 associated LSH mutants and wild-type LSH to the engineered Oct4 locus in the CIP system after rapamycin treatment at indicated time points using V5 antibody (n = 3 independent experiments). Cells lacking LSH fusion protein expression served as controls. Data are represented as mean ± SD. d Flow cytometry was used to measure reporter-GFP expression in ICF4 derived LSH mutants CIP system compared to that in wild-type or ATP mutant LSH (K 237 A) CIP system after 0 (red) and 5 (blue) days treatment of rapamycin. e ChIP-qPCR analysis to assess the dynamic changes of macroH2A1, macroH2A2 and H2A enrichment at the CiA: Oct4 locus in the engineered mouse ES cells tethered with ICF4 associated LSH mutants or wild-type LSH with rapamycin treatment for 0 and 5 days (n = 3 independent experiments). Data are represented as mean ± SD. Significance assessed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (wild type: *adjusted p < 0.05, ** adjusted p < 0.01 and ***adjusted p < 0.001; Q 682 R: ❖adjusted p < 0.05 and ❖❖adjusted p < 0.01; L 784 del: #adjusted p < 0.05). f Flag-IP of indicated proteins confirmed by western blot analysis in U2OS cells with a stable expression of wild-type Flag-LSH or ICF4 associated Flag-LSH mutants. Cells without a stably integrated of Flag-LSH expression vector served as controls. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.