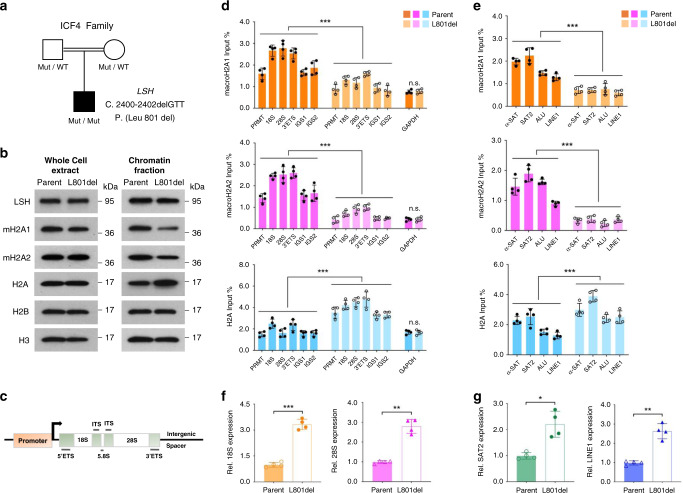
Fig. 7. Human ICF4 mutant cells display impaired macroH2A deposition associated with transcriptional de-repression at repeats.
a Schematic representation depicts a human homozygous Leu 801 del (L 801 del) LSH mutant ICF4 patient family tree. Both parents are heterozygous for the mutated allele. b Western blot analysis for detection of indicated proteins in whole-cell extract or chromatin fraction isolated from ICF4 (L 801 del) patient and parental (Parent) lymphocyte cells. c, d Schematic representation of human rDNA repeated locus (c). PRMT promoter, ETS external transcribed spacer, ITS internal transcribed spacer, IGS intergenic spacer. ChIP-qPCR analysis shown in d for detection of macroH2A1, macroH2A2 and H2A enrichment at rDNA sequences in ICF4 patient cells compared to parental control cells. ***p < 0.0001. e ChIP-qPCR analysis for detection of macroH2A1, macroH2A2 and H2A enrichment at repeat sequences (satellite sequences, ALU and LINE1 elements) in ICF4 (L 801 del) and parental cells. ***p < 0.0001. f, g RT-qPCR analysis for detection of transcriptional levels at rDNA (18S, ***p = 0.0003; 28S, **p = 0.0051; f) and repeats (SAT2, *p = 0.0104; LINE1, **p = 0.0048; g) in ICF4 mutant cells compared to parental lymphocyte cells. Data are represented as mean ± SD. Paired two-tailed Student’s t test (d–g). d–g representative of four independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.