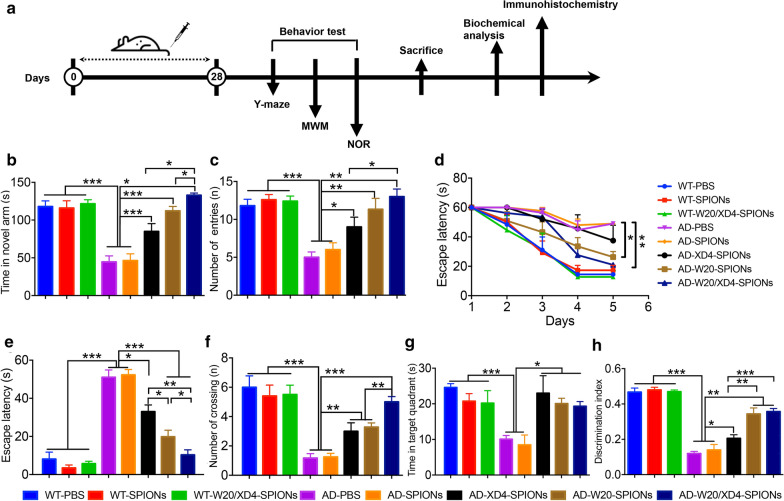
Fig. 3.
W20/XD4-SPIONs rescued cognitive deficits in AD mice. a Schematic representation of pharmacological treatment and experimental measurement. b, c The short-term memory of AD mice and their WT littermates treated with various SPIONs was measured by Y-maze. The time spent in the novel arm (b) and the number of entries (c) were recorded. d–g Spatial learning and memory retention of AD mice and their WT littermates treated with various SPIONs were assessed using the Morris water maze. d During training trials, the latency to find the hidden platform was measured. During probe trials, the latency to the position of the removed platform (e), the number of platform crossings (f) and the time spent in target quadrant (g) were determined. (h) The object recognition test was performed in AD mice and their WT littermates treated with various SPIONs. The results were expressed as discrimination index. n = 8 mice/group. Data represent means ± SEM and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test (b, c, e–h) or two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test (d). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001