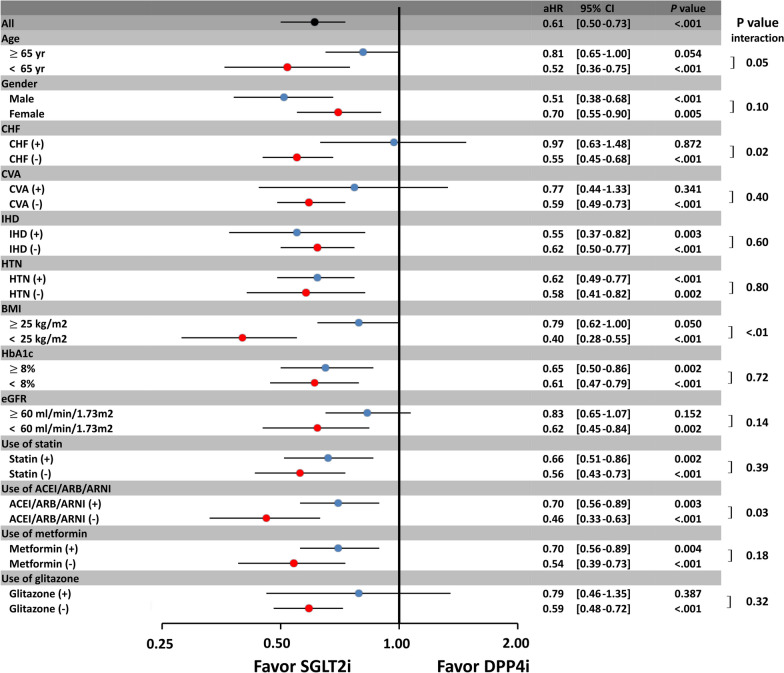
Fig. 3.
Subgroup analysis of forest plot of hazard ratio (HR) for SGLT2i versus DPP4i among T2DM patients after IPTW. Subgroup analysis showed consistent results for a lower risk of incident AF for SGLT2i vs. DPP4i among T2DM patients aged 65 years, female in gender, and those with cerebral vascular disease (CVA), ischemic heart disease (IHD), hypertension (HTN), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) 8%, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 ml/min/1.73 m2, and the use of concomitant medications as the main analysis (P interaction > 0.05). Of note, the use of SGLT2i reduced the number of new-onset AF events in subgroups including those without previous history of heart failure, those with BMI < 25 kg/m2, and those without concomitant use of renin-angiotensin system blockers (P interaction < 0.05). ACEI = angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB = angiotensin receptor blocker; ARNI = angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor; BMI = body mass index; CHF = congestive heart failure; CVA = cerebral vascular disease; eGFR = estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c = hemoglobin A1c; HTN = hypertension; IHD = ischemic heart disease. Other abbreviations as in Figs. 1 and 2