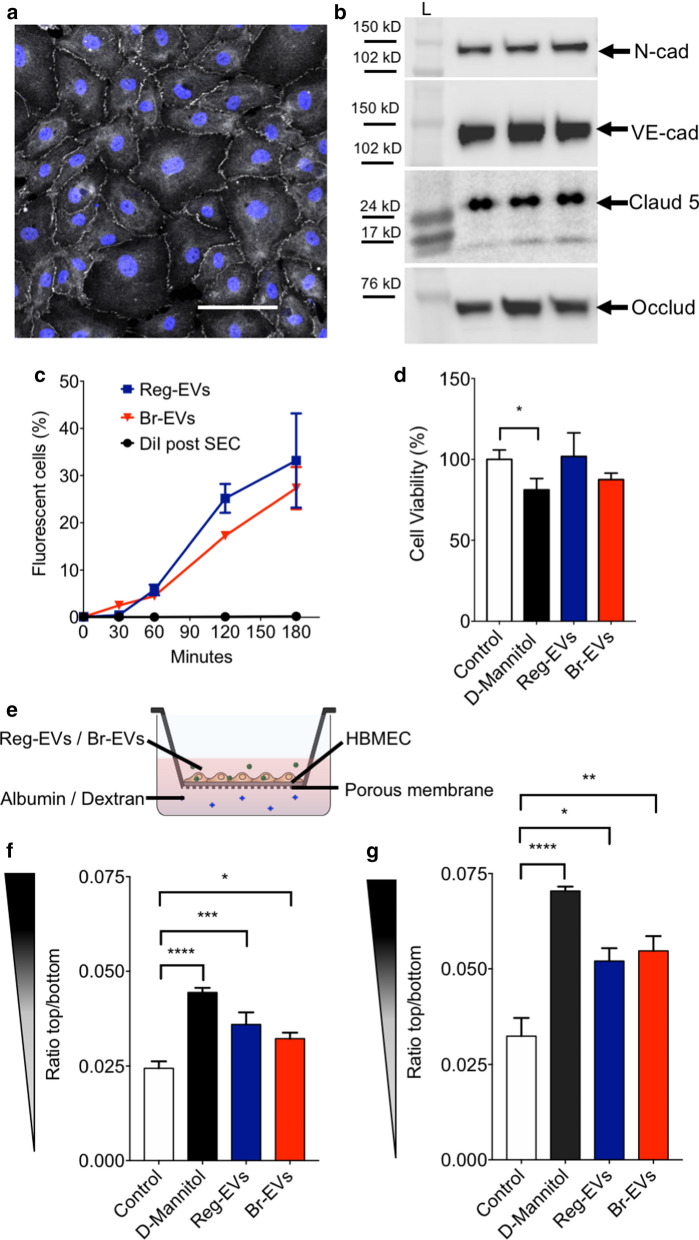
Fig. 2.
Effects of breast cancer cell-derived Reg-EVs and Br-EVs on brain endothelial cells. Reg EVs were derived from MDA-MB-231 cells and Br-EVs from MDA-MB-231-BrM2-831 cells. a Confocal analysis zona occludens 1 (white) in human brain microvascular endothelial cell (HBMEC) monolayers. Nucleus labelled by Hoechst is displayed in blue. Scale bar, 100 μm. b Western blot expression of endothelial tight junction proteins, (N-cadherin, VE-cadherin, claudin-5, and occludin) in three HBMEC replicates. Black rectangles represent the expected molecular weight ranges for the proteins. Claud5 claudin 5, L Protein ladder, N-cad N-cadherin, Occl occluding, VE-cad VE-cadherin. c Time-dependent uptake of fluorescently labeled EVs in HBMECs analyzed by flow cytometry. DiI, 1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′ tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate. d HBMEC viability following exposure to D-mannitol (positive control) or EVs for 24 h. e Schematic of the transwell experiment. f, g Passage of fluorescently labeled albumin (f) or dextran (10 kD) (g) through HBMEC monolayers after three hours of incubation. HBMEC monolayers were pre-exposed to D-mannitol or EVs for 24 h. D-mannitol dose, 200 mM; EV dose, 104 EVs/cell. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three (c, f, g) or four (d) replicates. Statistical analysis was performed by a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test (c) or a one-way ANOVA test (d, f, g) with post-hoc pairwise comparisons calculated with a Tukey’s test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001