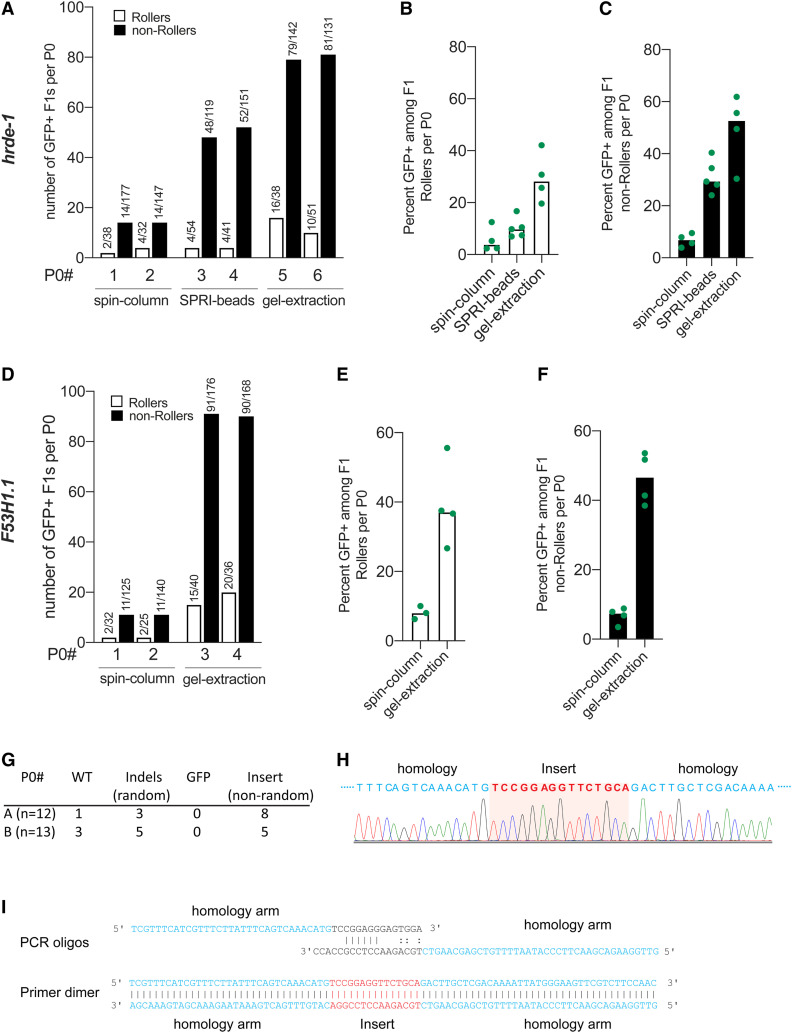
Figure 3.
Purity of donor DNA is crucial for best HDR efficacy. HDR efficiencies of donors prepared by different methods of purification are plotted for hrde-1 and F53H1.1. (A) Number of GFP+ F1 Rollers and non-Rollers from two representative broods are plotted. GFP+ animals among, (B) Rollers, and (C) non-Rollers is plotted as percentage of animals scored in each cohort per brood. Similarly, (D–F) HDR efficiencies are plotted for F53H1.1 locus. (G) Insertions and deletions identified at hrde-1 target site in F1 Rollers from two P0s (spin-column), (H) Sanger sequencing trace of the 15 bp nonrandom insert for a homozygous F2 animal. Partial homology arms of the donor are shown in blue, and the sequence that got inserted into the genome is shown in red. (I) Schematic representation of predicted primer dimer formation is shown with 6 bp perfect match and mismatched 3′ tails. Part of each oligo that is homologous to the PCR template plasmid is shown in black (linkers on either end of gfp) and the homology arms are shown in blue and the sequence (Insert) that would get inserted through HDR is shown in red. All the donors were 5′ TEG-modified and melted. Gel-purified donors were further cleaned-up with SPRI beads (see File S1).