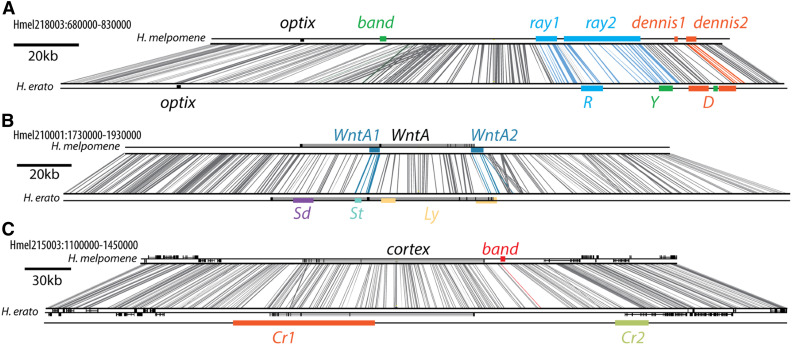
Figure 7.
ACT-BLAST alignment of three color pattern regions between H. melpomene and its comimic H. erato. In each panel, the H. melpomene scaffold (top) is compared to the H. erato scaffold (bottom) with each BLAST hit connected by a line. H. melpomene is annotated with elements identified herein, and H. erato is annotated with elements controlling convergent phenotypes as identified in Van Belleghem et al. (2017). In (A) one of the H. melpomene elements associated with the ray pattern element (blue; ray2 in H. melpomene; R in H. erato) contains homologous sequence with the ray pattern element in H. erato, as indicated by the connecting colored lines. As does one of the elements associated with dennis pattern in H. melpomene and the H. erato dennis associated element (orange; dennis2 in H. melpomene; D in H. erato) (Table S20). The elements associated with band (green; band in H. melpomene; Y in H. erato) are in distant positions, but H. erato Y is situated in conserved sequence which is included in the H. melpomene ray2 element. In (B) the H. melpomene WntA1 and WntA2 elements both contain homologous sequence to the H. erato elements St and Ly (Table S20). In (C) band is shown to not be homologous to either of the previously identified elements (Cr1 and Cr2) in H. erato. H. erato elements are colored based on scheme used in Van Belleghem et al. (2017).