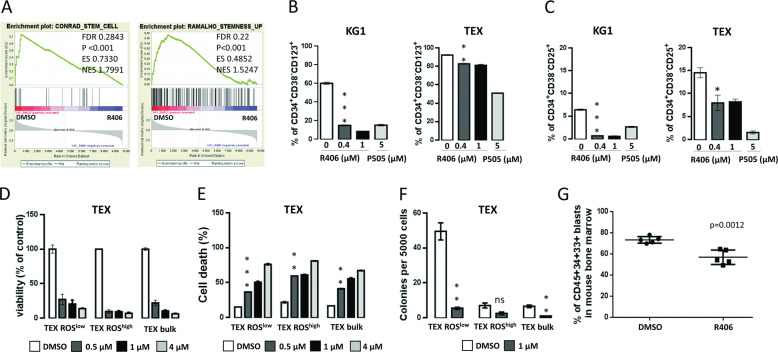
Fig. 4. SYK inhibition targets leukemia stem cells (LSC)-enriched acute myeloid leukemia (AML) subpopulations.
A GSEA plots showing downregulation of stem-cell transcriptional program in KG1 and MOLM14 cell lines after R406 treatment. Source data were derived from the publicly accessible dataset available from GEO at the accession number GSE46302. B, C KG1 and TEX cells were incubated with the indicated concentration of R406 or P505 for 48 h, then the expression level of either CD25 or CD123 in CD34+CD38−-gated population was assessed by flow cytometry. The experiment was repeated twice. Bars represent mean + /− SD from two biological replicates of a representative experiment. P value was calculated using Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. D, E Sorted ROS-low, ROS-high and bulk TEX cells were treated with vehicle or increasing concentration of R406 for 3 days. Thereafter, cells were analyzed by MTS assay to assess cell proliferation (D), or stained with PI followed by flow-cytometry analysis to assess cell death (E). In D, the results are shown relative to DMSO-treated control and represent mean + /− SD from three biological replicates. In E, the percentage of PI-positive cells is shown. The experiment was repeated twice. Bars represent mean + /− SD from two biological replicates of a representative experiment. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. F In total, 5 × 103 of sorted ROS-low, ROS-high, and bulk TEX cells were plated in GFH4434 medium containing either DMSO or R406 (0.17 µM). Colonies consisting of a minimum of ten cells were counted 14 days after plating. Graph shows the mean number of colonies (+/− SD) obtained from two independent plates. **P < 0.01. G Primary AML blasts (from patient 096/17) were cultured ex vivo for 24 h with DMSO or 4 µM of R406. Thereafter leukemia cells were transplanted into NSG/J mice (n = 5 per group). Mice were killed 8 weeks after transplantation, and AML engraftment was assessed by FACS analysis for the presence of human CD45+CD33+CD34+ cells in mouse bone marrow. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t test.