Figure 3. Estrogen inhibits oxidative stress induced tau cleavage in ONHAs.
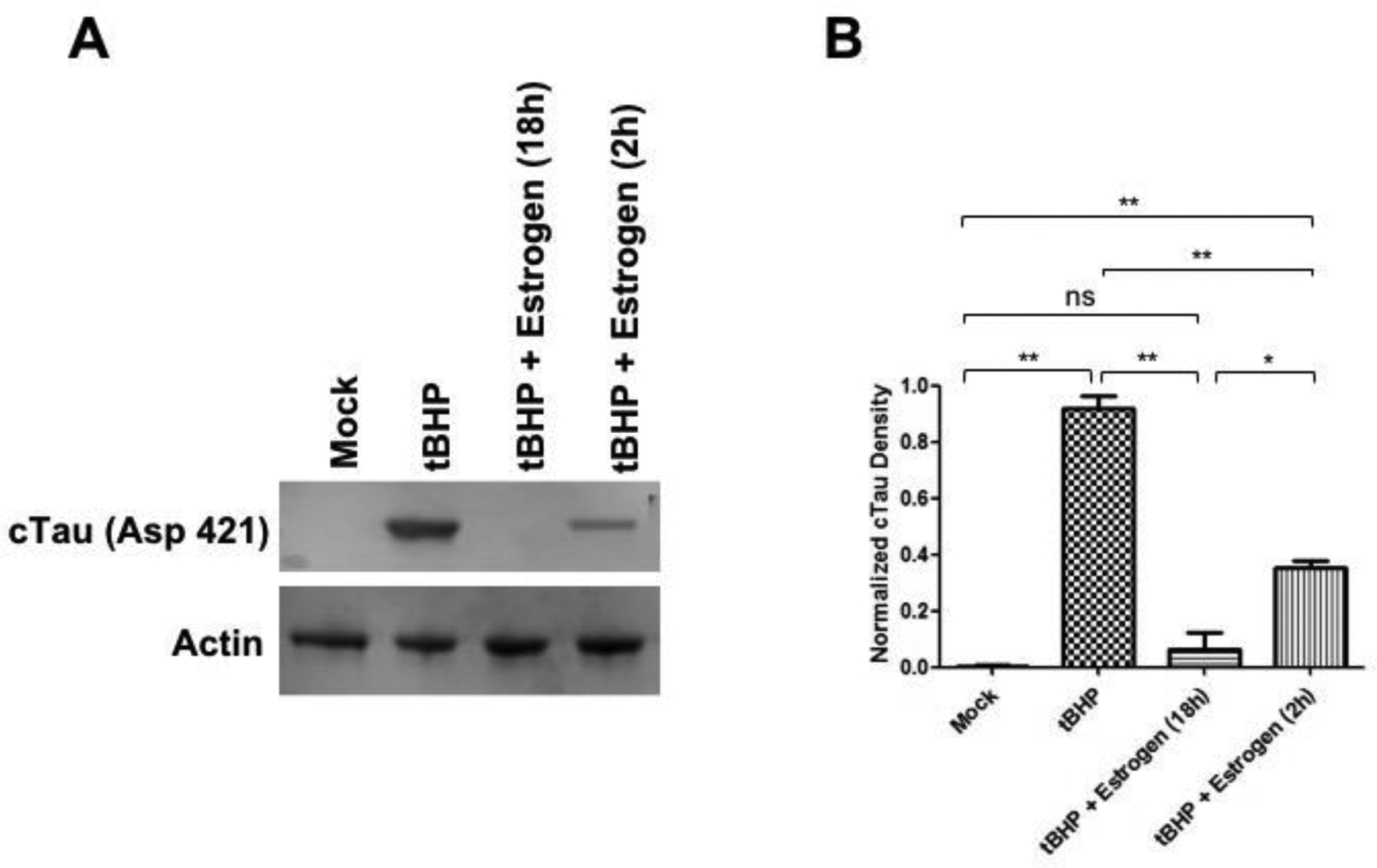
ONHAs were pretreated with 25 μM estrogen followed by induction of oxidative stress with tBHP. (A) tBHP treated ONHAs were used in immunoblotting assays to measure cleaved tau (cTau) levels. For a loading control actin was used. (B) tBHP treated ONHAs had a significant amount of cTau compared to mock treated (**, p=0.0025). Estrogen pretreatment for 2 h led to a significant decrease in detectable cTau (**, p=0.0083). Estrogen pretreatment for 18 h further decreased cTau levels significantly (**, p=0.0078). Pretreatment with estrogen for 18 h was more effective than a 2 h pretreatment in attenuating cTau levels (*, p=0.0486). ONHAs pretreated with estrogen for 2 h still showed a significant amount of cTau compared to mock (**, p=0.0055). Pretreatment of ONHAs for 18 h had no significant difference from mock (ns, p=0.4565). Experiments were done in triplicate (n-=3) and values were depicted as mean +/− SEM and analyzed using ANOVA (p=0.0003). For statistical comparison, the Bonferroni post-hoc test and Student t-test were used. Statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
