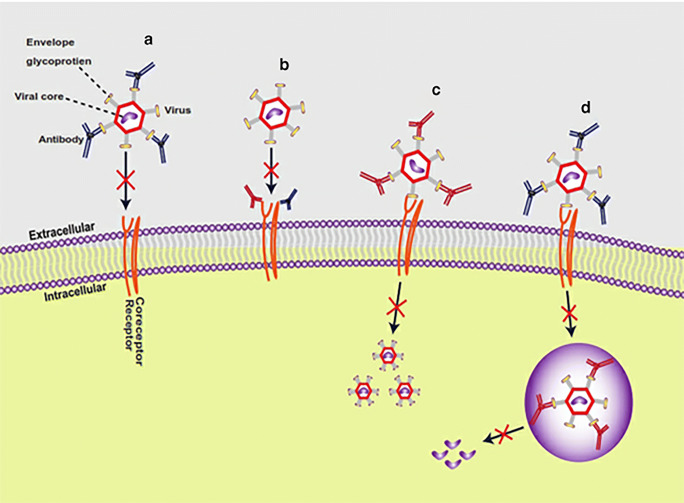
Fig. 2.
Modes of viral neutralization. Antibodies neutralize viruses by several mechanisms, either inhibition of virus entry into host cells as (a) Antibodies bind to an epitope in the viral glycoprotein envelope, lead to inhibit attachment to host cells. (b) Antibodies through the fab region can bind to host cell receptors or coreceptors (have Fcγr)) lead to inhibit viral entry. Or post binding inhibition of antibody-virus complex as (c) antibodies can bind to a non-binding region in the virus envelope lead to inhibit the conformational change to allow membrane fusion. (d) for certain viruses that need low endosomal PH for conformational change, antibodies bind to viral inside the endosome lead to inhibit the change in PH to achieve the membrane fusion, and antibodies can inhibit the release of the viral virion