Fig. 1. The regulation of m6A modification.
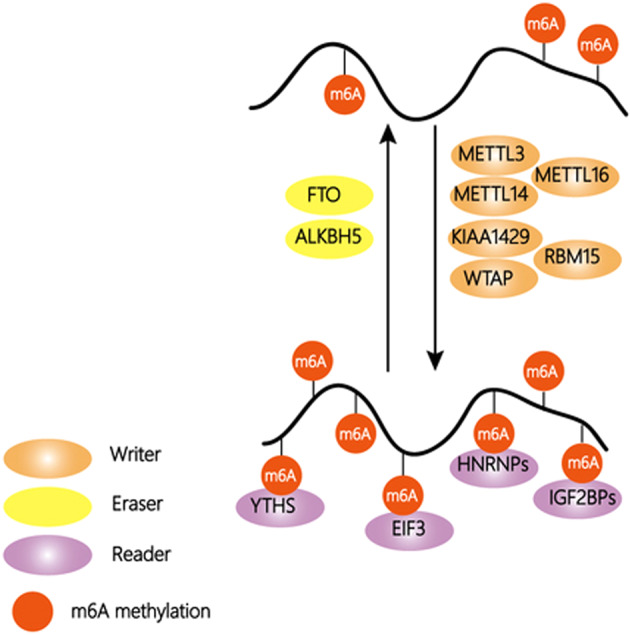
M6A is added, removed and recognized by its writers, erasers and readers. METTL3-METTL14 is the core of the methyltransferase and functions in cellular m6A deposition on nuclear RNAs. WTAP is a subunit of the methyltransferase, which promotes the recruitment of the m6A methyltransferase complex to mRNA targets. KIAA1429 and RBM15 (RNA binding motif protein 15) are also required for the above process. FTO and ALKBH5 are two enzymes capable of removing m6A, exhibiting efficient oxidative demethylation activity of abundant m6A in RNA. YTH domain family, HNRNP protein family, IGF2BPs and eIF3 bind to m6A-modified RNA through conserved m6A-binding domains and play different roles in RNA metabolism.
