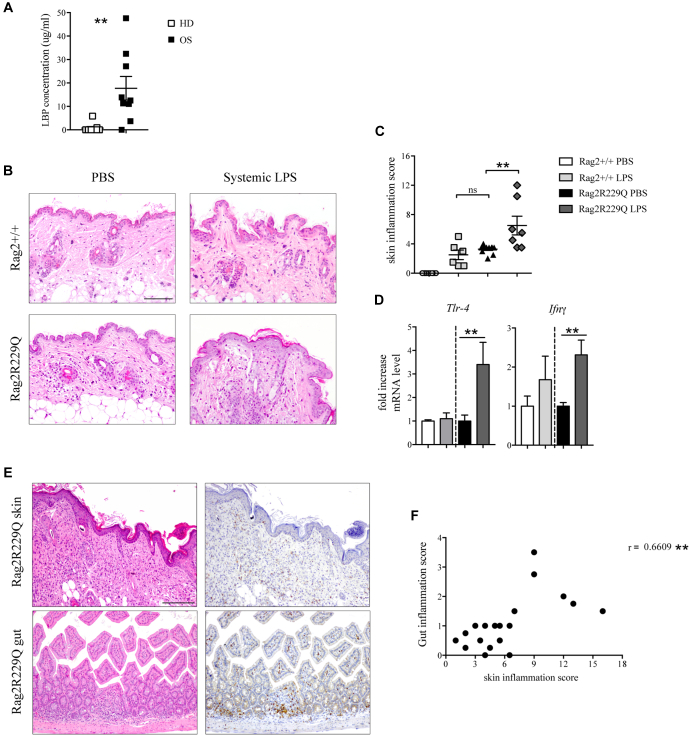
Fig 6.
Systemic LPS triggers cutaneous inflammation. A, LPS-binding protein (LBP) concentration in the sera of patients with OS and HDs (n = 8-9 from 2 experiments). B,Rag2+/+ and Rag2R229Q mice received a single injection of 100 μg LPS intraperitoneally and were sacrificed 24 hours later. Representative skin sections from systemic LPS-treated and untreated Rag2+/+ and Rag2R229Q mice stained with H&E. Bar = 200 μm. C, Histogram shows the inflammation score in the skin of n = 6-11 mice/group from 2 experiments. D, Fold increase of Ifng and Tlr4 on skin tissue (n = 6-8 mice/group from 2 experiments). E, Representative small intestinal and skin sections from Rag2R229Q mice with erythroderma stained with H&E and CD3 immunostaining. Bar = 200 μm. F, Correlation between intestinal and skin inflammation scores of Rag2R229Q mice manifesting or not evident cutaneous manifestations (black dots). The Spearman r value is indicated in the graph (n = 10 mice). Values are mean ± SEM. ∗∗P < .01. Statistical analysis was performed using Mann-Whitney U test.