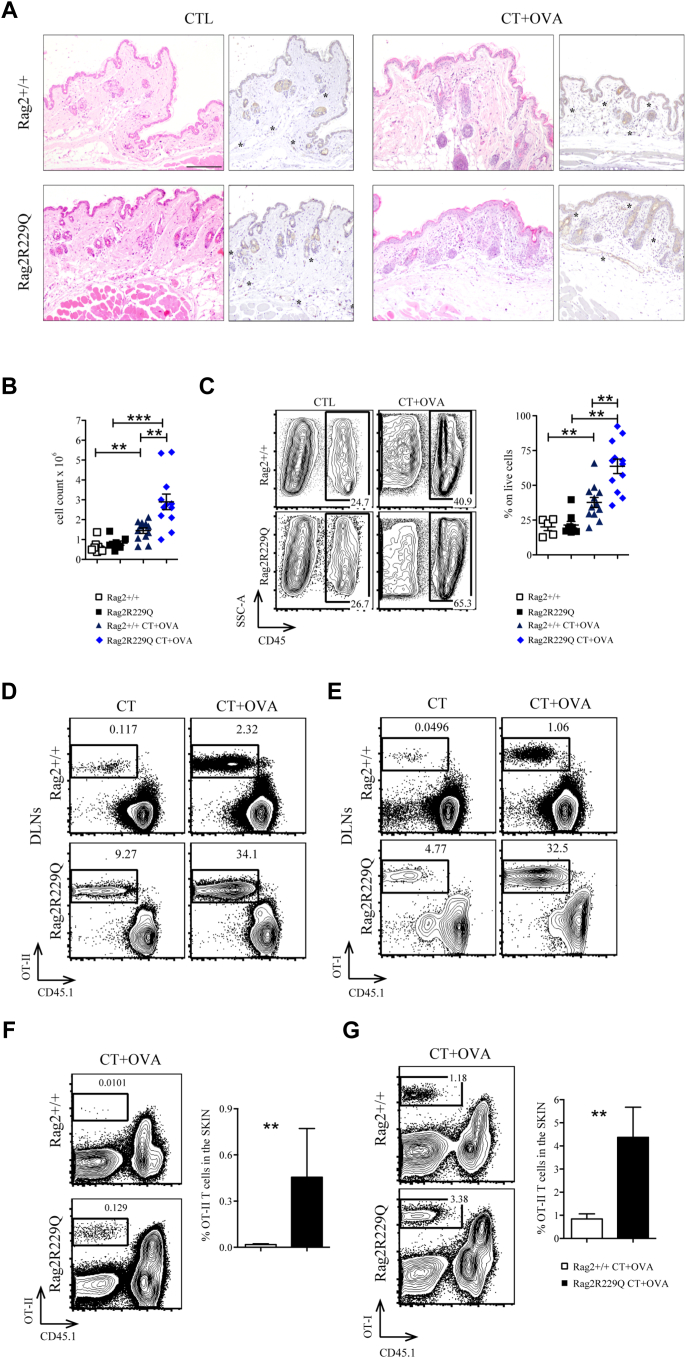
Fig E4.
Cutaneous inflammatory environment in mutant mice promote T-cell infiltration. A, Representative skin section from controls and CT+OVA-treated Rag2+/+ and Rag2R229Q mice stained with H&E and CD31 immunostaining (asterisks mark the CD31-positive vessels). Bar = 200 μm. B, Total skin counts from skin suspension (n = 5-12). C, Representative FACS plot and frequencies of CD45+ cell population of skin suspension (n = 5-12). D and E, CD4 or CD8 splenocytes from OT-II or OT-I mice were adoptively transferred into Rag2+/+ and Rag2R229Q recipients. Topical immunization was applied on ears once with OVA plus CT or only CT. Recipient mice were sacrificed after 7 days. Representative dot plots of donor-derived OT-II or OT-I cells within total live population of DLN suspension. F and G, Representative dot plots and frequencies of donor-derived OT-II or OT-I cells within total live population of skin suspension (n = 5-7 mice/group). Values are mean ± SEM. ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001. Statistical analysis was performed using Mann-Whitney U test.