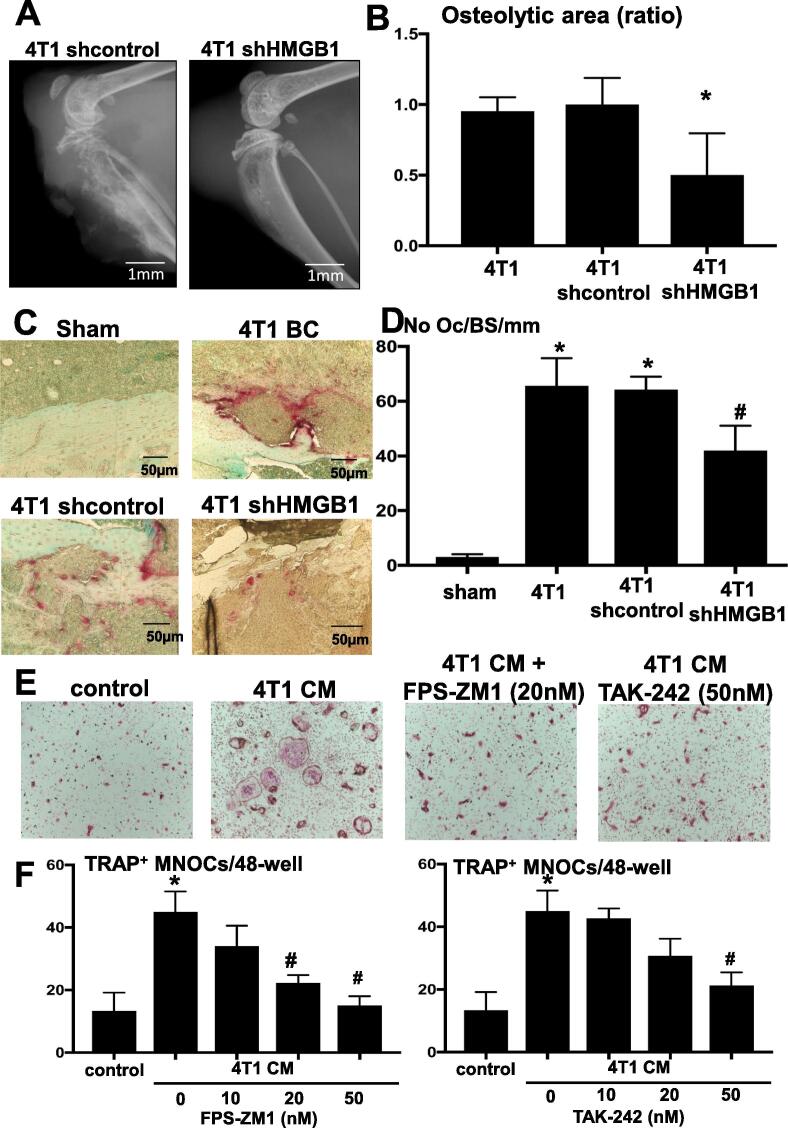
Fig. 5.
Effects of HMGB1 on osteoclastic bone destruction associated with 4T1 BC colonization in tibiae. (A) Osteolytic lesions in tibiae of mice inoculated with 4T1/sh control (left) and 4T1/sh HMGB1 cells (right). Radiographs were taken at day 15 after intratibial cell inoculation (1 × 105 cells/10 μl). Scale bar 1 mm. (B) Quantitative evaluation of osteolytic lesions in tibiae of mice inoculated with 4T1/sh control and 4T1/sh HMGB1 cells seen in Fig. 4A. The area of osteoclastic bone destruction in tibiae was determined on radiographs using Image J. Osteolytic area (ratio) on Y-axis in the figure represents, area of 4T1/sh control or 4T1/sh HMGB1/area of 4T1 in which area of 4T1 is designated as 1. The area of osteolytic lesions associated with 4T1/sh HMGB1 cells were significantly smaller than those of 4T1 and 4T1/sh control. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 8). * Significantly different from sham control and 4T1/sh control mice (p < 0.05). (C) Histological pictures of the osteolytic lesions stained with TRAP. TRAP+OCs at tumor-bone interface at endocortical bone are stained in red. Scale bar 50 µm. (D) Quantitative analysis of the number of TRAP+ OCs formed in Fig. 4C. The number of OCs present at tumor-bone interface at endocortical bone was determined in three levels of histological sections for each sample under a microscope as described previously [24] and is shown on Y-axis as No OC/Bone Surface (BS)/mm in the figure. The number of TRAP+OCs in osteolytic lesions associated with 4T1/sh HMGB1 cells was significantly less than that of 4T1 and 4T1/sh control. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 4). * Significantly different from sham mice (p < 0.05). # Significantly different from 4T1 mice and 4T1/sh control mice (p < 0.05). (E) Effects of 4T1 BC CM, FPS-ZM1 (RAGE antagonist) and TAK-242 (TLR4 antagonist) on TRAP+MNOC formation. Bone marrow macrophages (1 × 105 cells/48-well) were cultured with or without 4T1 BC CM (20%, v/v) and in the absence or presence of FPS-ZM1 (20 nM) and TAK-242 (50 nM) with supplementation of suboptimal dose of M-CSF (30 ng/ml) and RANKL (10 ng/ml) for 5 days. Wells were then stained for TRAP. 4T1 BC CM increased TRAP+MNOC formation, which was decreased by treatment with FPS-ZM1 and TAK-242. (F) Quantitative analysis of TRAP+MNOC formation in bone marrow macrophage cultures seen in Fig. 4E. Cultures were treated with increasing doses (10, 20 and 50 nM) of FPS-ZM1 and TAK-242 for 5 days. The number of TRAP+MNOCs was counted under a microscope. FPS-ZM1 significantly decreased TRAP+MNOC formation in a dose-dependent manner, while TAK-242 significantly decreased it only at 50 nM. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 4). * Significantly different from control (p < 0.01).# Significantly different from 4T1 CM (p < 0.05). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)