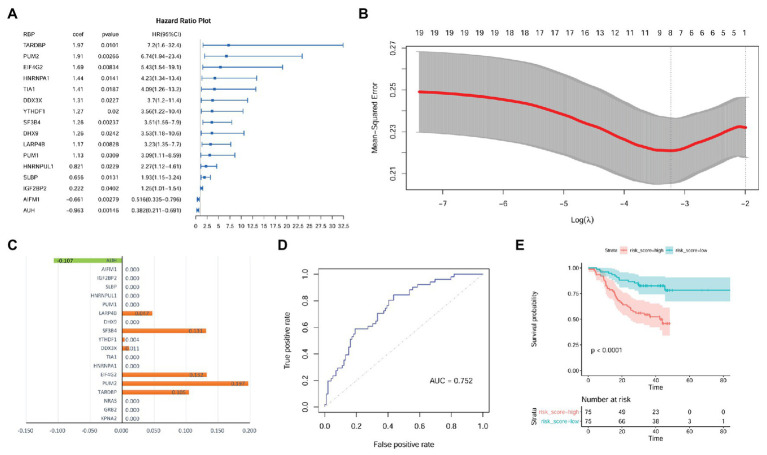
Figure 8.
Identification of prognostic signature with RBPs of KPNA2, GRB2, and NRAS in HCC at protein level. (A) Gender, age, and tumor size corrected prognostic effects of RBPs of KPNA2, GRB2, and NRAS on HCC overall survival, and the right part was the visualization of the HR (95% CI). (B) Tuning parameter lambda (λ) selection using 10-fold cross validation. (C) Eight RBPs with absolute value of coefficient >0 were included in the LASSO regression model. The x-axis represented the coefficients of the RBPs, and the y-axis indicated the RBP variables. (D) The LASSO regression model could predicate the survival status with an AUC of 0.752 through ROC curve analysis. (E) HCC patients with higher risk score were indicated to have a shorter survival than those with lower risk score. RBPs, RNA-binding proteins; HR, hazard ratio; AUC, area under the curve; ROC, receiver operating characteristic. Ezcox package in R were used for Cox regression analysis of the RBPs (A) with the RBP expressions as covariates and age, gender, and tumor size as controls. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with log-rank test (E) was used for the overall survival comparison between patients with high and low risk score, and the median value of the risk score was used as threshold for grouping the patients. For the analysis, p < 0.05 was considered significant.