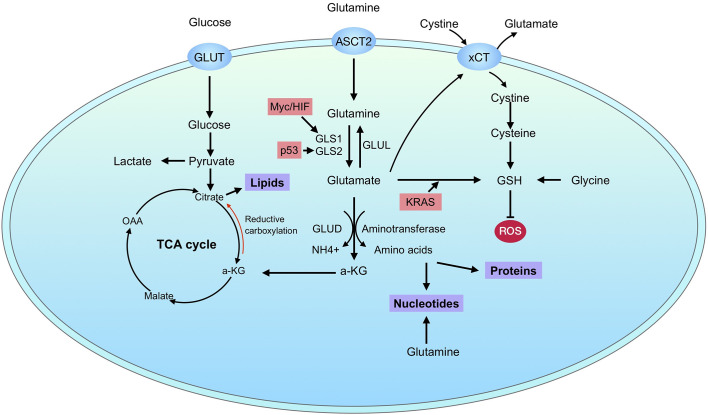
Figure 2.
Glutamine metabolism in cancer. Cancer cells uptake glucose and glutamine through GLUT and ASCT2, respectively. After transporting into cells, glutamine is catalyzed to glutamate by glutaminases, which have two isoforms: GLS1 and GLS2. Glutamate is further converted to α-KG through GLUD or aminotransferases. The resulting metabolites can supply for bioenergetics through tricarboxylic/critic acid (TCA) cycle and support biosynthesis of proteins, nucleotides and lipids. In addition, glutamine metabolism also contributes directly to GSH synthesis. The regulation of glutaminase is marked in pink.