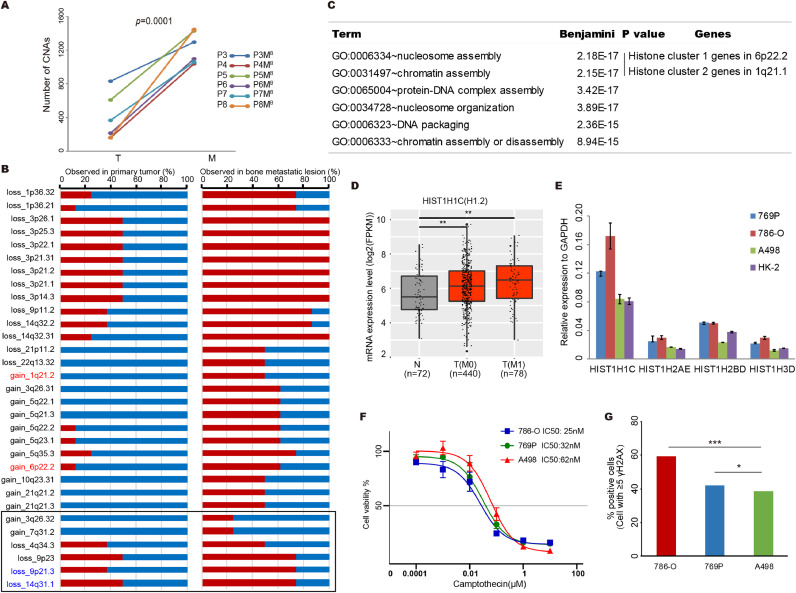
Fig. 4.
Increased chromosomal instability characterizes metastatic renal cell carcinoma evolution with therapeutic relevance. (A) The metastatic lesions have larger number of focal SCNAs compared to matched primary tumour in patient 3 to 8. Statistical significance is evaluated by Student's t-test. (B) Selected SCNAs during metastatic progression. For each SCNA event, the percentage of observed numbers in primary and metastatic tumors in the 8 m-ccRCC patients are plotted. The red box represents the observed pencentage of each SCNA event in primary or metastatic tumors of all patients. Previous reported enriched SCNA events in metastatic tumors are highlight. (C) The GO pathway analysis with all the genes within the selected gain copy number regions presented in (B). The enriched GO names, adjusted p value and enriched gene clusters of each pathway are listed. Histone cluster 1 and 2 genes are involved in nucleosome assembly and chromatin assembly pathways. (D) Expression levels of HIST1H1C (H1.2) gene in normal kidney tissues, primary tumor tissues of M0 or M1 stage ccRCC patients are plotted. Expression of HIST1H1C (H1.2) in primary tumor tissue (M0 and/or M1) of ccRCC patients are significantly higher than normal kidney tissues. The gene expression datasets are downloaded from TCGA. N presents the normal kidney tissues, T (M0) presents primary tumors from non-metastatic ccRCC patients and T (M1) presents primary tumors from metastatic ccRCC patients. The sample size of each group was indicated. Statistical significance was evaluated by Student's t-test. * p<0.05, **p<0.01.(E) mRNA levels of histone cluster genes in ccRCC cell lines and human renal tubular cells HK-2. Expression levels are shown as fold differences (mean ± SD) compared to GAPDH. (F) Growth curves for ccRCC cells with varying expression of histone cluster genes after 72hr exposure to camptothecin. (G) DNA double stand break induced by camptothecin treatment for ccRCC cells with varying expression of histone cluster genes.