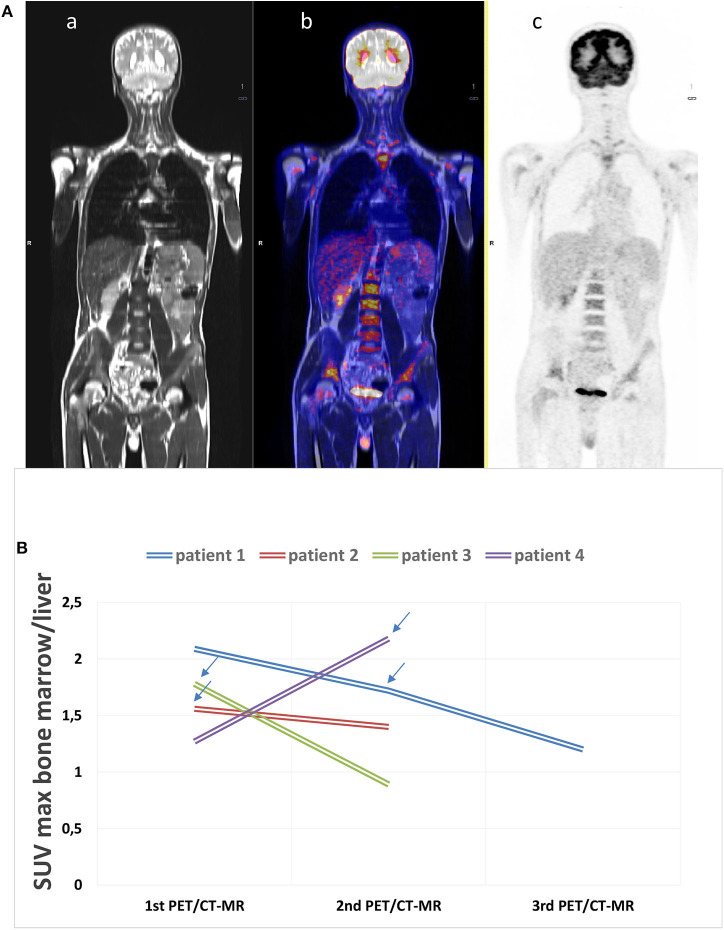
Figure 1.
(A) Example of an 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography with magnetic resonance (PET/CT-MR) scan at disease onset. (a) MR whole-body image, T1 turbo spin echo, coronal (WB_t1_tse_cor), (b) fused image, and c) PET acquisition image with attenuation correction (PET_AC). This scan shows a diffusely increased FDG uptake in the bone marrow (SUVmax 4.12), in the spleen (SUV max 3.13), and in the submandibular lymph nodes (SUVmax 5.61). The patient was diagnosed with adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) and started therapy with glucocorticoids after acquiring the images. (B) 18F-FDG PET/CT-MR was repeated in four patients. The arrows state the moment IL-1 inhibitory therapy was started during the follow-up showing the decrease in bone marrow uptake.