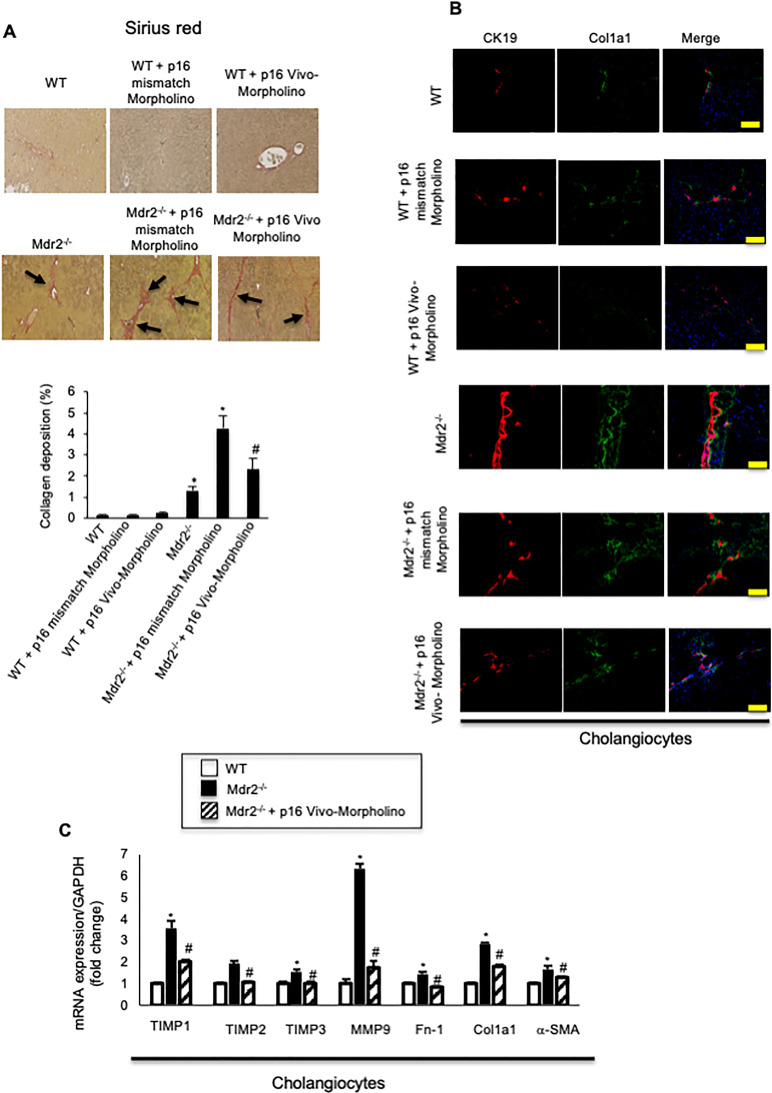
Figure 5.
(A) There was increased collagen deposition in Mdr2−/− compared to WT mice, which decreased in Mdr2−/− mice treated with p16 Vivo-Morpholino compared to Mdr2−/− mice treated with mismatch Morpholino. Ten different fields from three samples from three different animals were analyzed. Original magnification: 20×. *p < 0.05 versus WT mice. #p < 0.05 versus Mdr2−/− mice. Black arrows show collagen deposition around bile ducts. (B) By immunofluorescence, there was increased immunoreactivity of Col1a1 in Mdr2−/− compared to WT mice, which decreased in Mdr2−/− mice treated with p16 Vivo-Morpholino sequences compared to Mdr2−/− mice treated with mismatch Morpholino. Col1a1 (green staining); CK19 (red staining); nuclei were stained with DAPI; scale bar: 100 μm. *p < 0.05 versus WT mice. #p < 0.05 versus Mdr2−/− mice. (A, B). There were no changes in liver fibrosis between WT mice treated with p16 mismatch Morpholino and p16 Vivo-Morpholino. (C) By real-time PCR, the mRNA expression of fibrosis markers Fn-1, Col1a1, a-SMA, TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, and MMP9 increased in cholangiocytes from Mdr2−/− compared to WT mice, but decreased in Mdr2−/− mice treated with p16 Vivo-Morpholino compared to Mdr2−/− mice. Data are mean ± SEM of three evaluations performed in a cumulative preparation of cholangiocytes from four mice. *p < 0.05 versus WT mice. #p < 0.05 versus Mdr2−/− mice.