Fig. 2.
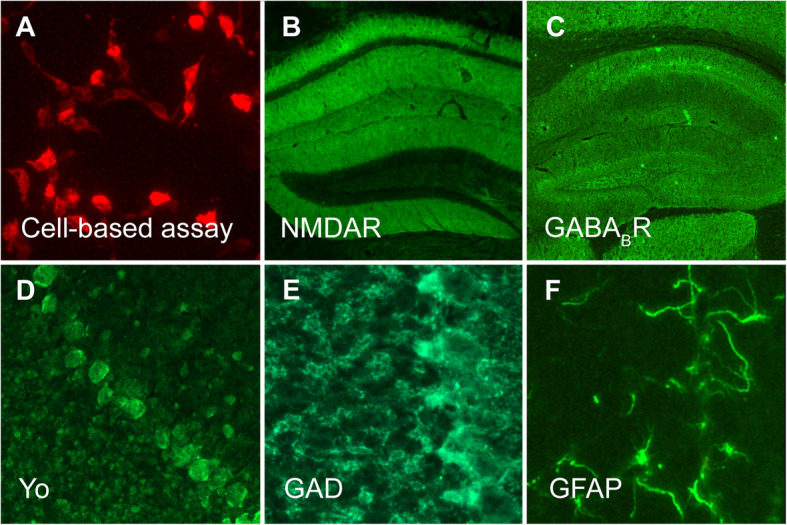
Detection of anti-neuronal autoantibodies for the diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. a The current gold standard for established surface antibodies is the cell-based assay (CBA), in which diverse target antigens (in this example NMDAR) are recombinantly expressed on the surface of cultured cells. Binding of patient antibodies from CSF or serum samples can be visualized with fluorescent dyes. b The same CSF sample of a patient with NMDAR encephalitis shows strong binding on a mouse hippocampus section with the characteristic NMDAR distribution. c Autoantibodies to GABAbR also show strong binding to hippocampus tissue, but with a clearly distinguishable pattern. d Antibodies to onconeural antigens can be visualized by staining of line blots (not shown) or by their intracellular binding on brain sections, here Yo antibody-positive Purkinje neurons on a mouse cerebellum section. e GAD antibodies show a punctate pattern around cerebellar granule cells and Purkinje neurons. f Immunohistochemistry using brain sections also allows the detection of antibodies targeting glia cells, such as against GFAP. The methodology further permits detection of as yet undetermined anti-brain antibodies in research laboratories. D and E modified from “Prüss et al. 2017, Neurotransmitter”
